Deception and Continuous Training Approach for Web Attack Detection using Cyber Traps and MLOps
- Information Security Laboratory, University of Information Technology, Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam
- Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh city, Vietnam
Abstract
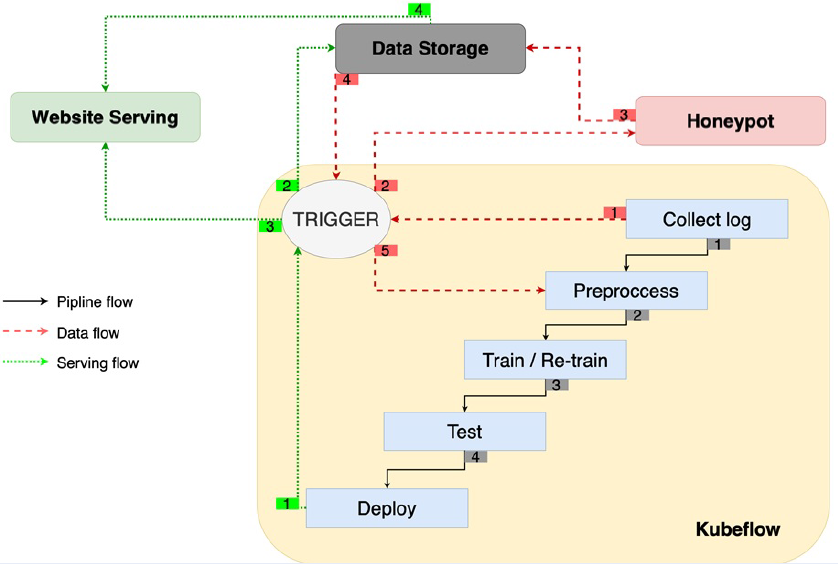
With the growth and expansion of the internet, web attacks have become more powerful and pose a significant threat in the cyber world. In response to this, this paper presents a deceptive approach for gathering malicious behavior to understand the strategies used by web attackers. The harmful requests collected through cyber traps or honeypots are analyzed and used to train machine learning (ML) models for web attack detection. Additionally, we implement an ML operations (MLOps) pipeline to automate the continuous training and deployment of these ML models in defensive systems. This pipeline trains the production model with newly collected data by using predefined triggers. Our experiments on two datasets, including Fwaf and our own, demonstrate that a proactive and continuous approach to tracking adversary behavior can effectively detect zero-day attacks, such as CVE-2022-26134 in web application servers.

