Enhancement of the crystalline phase in poly(vinylidene fluoride) by using the electrospinning technique and graphene oxide composition
- Phenikaa University Nano Institute, Phenikaa University, Ha Dong district, Hanoi, Viet Nam
- Faculty of Biological, Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Phenikaa University, Ha Dong district, Hanoi, Viet Nam
- Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Hanoi University of Industry, Bac Tu Liem District, Hanoi, Viet Nam
Abstract
Introduction: Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) possesses some unique characteristics, such as piezoelectric, ferroelectric, and pyroelectric properties. The β crystalline phase of PVDF exhibits the strongest piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties. In this study, the influence of the electrospinning process and graphene oxide (GO) composition on the β-phase formation of PVDF fibers is reported.
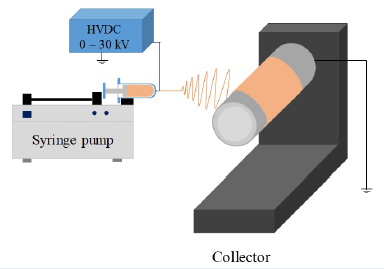
Methods: The morphology of electrospun PVDF and PVDF/GO fibers was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Characteristics of the crystal phase of electrospun PVDF and PVDF/GO fibers were analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).
Results: The PVDF fiber fabricated by the electrospinning technique had a crystallinity degree that increased by more than 117% compared to that of the precursor PVDF powder. The X-ray diffraction results show that the entire α phase of PVDF was converted to the β phase due to elongation deformation under the force of an electrical field during the electrospinning process. The presence of GO also induced the formation of the β phase of PVDF due to the interaction between the atomic groups on the surface of GO sheets and on the PVDF molecular chains.
Conclusion: Both the electrospinning process and GO led to an increase in the crystallinity of PVDF. PVDF/GO nanofibers with crystallinity degrees above 60% can be applied in many fields, such as water purification membranes, air filters, energy harvesting materials, biosensors, and catalysts.

