A comparison of the drying processes used to prepare bacterial cellulose for wound dressing applications
- Department of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, School of Biomedical Engineering, International University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is a promising polymer due to its ability to manage wound exudation and create a moist environment conducive to healing, alongside its high tensile strength. The natural form of BC hydrogel prevents it from maintaining its shape; therefore, water needs to be removed. The preparation of BC for wound dressing use often involves a drying process, which can significantly impact the final material’s properties. This article investigates the effects of drying methods on BC films, revealing structural changes in the membrane. Four different methods are selected, with methodical research on how drying affects physiological, morphological, and structural properties. The impact of each drying method on the physical, mechanical, and water-handling characteristics of BC is evaluated, providing insights into the optimal drying approach for achieving desirable wound dressing performance. The Oven Drying Method (ODM) alters BC’s structure, while the Freeze Drying Method (FDM) and Room Temperature Drying Method (RTDM) better preserve its morphology and mechanical integrity. Comparative analysis shows that ODM reduces elongation at break, whereas the Cold Drying Method (CDM) exhibits the highest elongation, indicating its suitability for wound dressings that require tensile strength within 1 to 32 MPa and a deformation capacity over 30%. As a result, CDM is appropriate for the preparation of BC films for use as wound dressings.
INTRODUCTION
Wound management is an essential aspect of healthcare, and advances in wound dressing materials have contributed to improving healing processes. A promising material for wound dressings is bacterial cellulose, as it possesses unique properties such as biocompatibility, high porosity, and excellent water absorption capacity. To fully exploit the potential of bacterial cellulose for wound dressing applications, it is crucial to carefully consider the drying process used during its preparation. This is because the drying process can significantly affect the structure, mechanical properties, and functionality of bacterial cellulose. Furthermore, different drying methods can lead to variations in the final product, affecting its effectiveness in wound healing. Variations in BC membrane characteristics that change under various drying techniques may influence the mechanical characteristics and chemical properties of BC, thus influencing the type of application.
The most common straightforward technique for dehydration is the oven drying method (ODM). However, the initial porous microstructure of the raw BC changed throughout these processes. The ODM membrane has a high crystallinity of more than 70%, and the SEM images show that the cellulose fibers are clear and oriented 1. Another drying method is freeze drying (FDM), which maintains the shape of the fiber due to the decreased surface tension 2.
In our study, we investigated the mechanical, chemical, and microstructural properties of BC membranes by comparing four distinct drying techniques to analyze the notable structural changes in BC. The cold drying method (CDM) involves cooling air in a drying cell below the freezing point on a cold surface, allowing the cold surface to retain moisture, and using dehydrated air for drying 3. According to this theory, the morphology of BC is expected to undergo a minor change, and the structure is expected to be preserved. The application at hand, as mentioned above, determines the drying process used. When dried at room temperature, BC films show less crystallinity and little to no change in fiber diameter 4. Therefore, the room-temperature drying method (RTDM) was used to collate the other drying methods as the control group. The final properties of the materials can be significantly influenced by selecting the appropriate drying technique, so it is possible to adjust the water adsorption capacity, fiber entanglement, or the amount of accessible hydroxyl groups. Therefore, the characteristics of BC films that were dried using various techniques (room temperature, freeze drying, cold drying, and oven drying) are necessary.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
MATERIALS
Fermented bacterial cellulose from was purchased from Minh Tam Co., Ltd., Vietnam. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (98%) was purchased from Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd., China. All compounds were used as they were without any additional changes.
METHODS
PURIFICATION OF BACTERIAL CELLULOSE (BC)
The raw BC membranes obtained from the Minh Tam Company were washed with DW three times to remove contamination and then soaked in 1 L of DW. Subsequently, the membrane was heated to 100°C for 2 hours and stirred with a magnetic stirrer. The BC membrane was cooled and immersed in 1 M NaOH for 24 h. The acetic acid was removed from the membrane, and the membrane was continuously washed with DW until it reached pH 7. The purified BC film was finally rinsed with DW, stored in a bag containing DW, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
PREPARATION OF THE DRIED BC MEMBRANE
There were four drying methods that followed after the purification process: ODM using drying and heating chambers—Binder ED115, Berlin, Germany—at 60 ± 1°C for 16 h; FDM using a vacuum freeze dryer—Labconco 7752020 series, US and Canada—at 42 ± 2°C with pressure at 0.12 mBar for 24 h; RTDM with UV light applied to both sides of BC for 1 h before drying at 26 ± 2°C for 144 h; and CDM using AnessicCatore cold dryer- model NWT-35, Italy, at 35 ± 2°C for 18 h with a dehydration temperature of -10°C and an air flow rate of approximately 4.0 m/s.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
The thicknesses of the purified BC films (4 cm × 4 cm) were measured before and after the drying process using an analytical balance, and the thickness was measured using an electronic digital caliper. For each sample, three repetitions of each measurement were performed to guarantee repeatability.
The BC water content was calculated using the following equation: (1)
Water loss (%) =
SURFACE MORPHOLOGY
The BC samples (1 × 1 cm) were observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM, JSM-IT100, JEOL, Japan) with an acceleration voltage of 10 kV. The BC samples were gold sputter coated prior to analysis.
CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to analyze the functional groups of the BC samples. (FTIR, Spectrum GX, PerkinElmer Inc., USA) in the wavenumber range of 4000-400 cm.
STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTICS
Using X-ray diffraction (XRD, D8 Advance, Brucker) with Cu Kα radiation, XRD patterns were obtained in the range of 2θ=10-80° with 0.02° steps and 0.5 s per step. The XRD deconvolution method, which separates the crystalline and amorphous contributions to the diffraction spectrum, can be used to calculate the crystallinity of BC.
The ratio of the integrated area under the XRD peaks to the integrated area of all the crystalline peaks can be used to determine the percentage of crystallinity of the samples using Origin Pro 2022.
The percentage crystallinity of BC was calculated using the following equation: (2):
% Crystallinity = I/(I+I) * 100 (2)
where the integrated intensities for the amorphous and crystalline phases are denoted by I and I, respectively.
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
The dried BC samples were cut into 1x5 cm pieces, and an electronic caliper was used to record the thicknesses. A texture analyzer was used to measure the mechanical strength (TA. XT plus, Stable Micro Systems, USA). Three samples in total, each with a maximum load of 1.0 N, were subjected to tests at a strain speed of 0.5 mm/min for each group.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Microsoft Excel was used to perform the statistical analysis, and Origin Pro 2022 was used to graph the data. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, and p < 0.05 was used to determine significant differences between methods. Student's t test was used for pairwise comparisons of normally distributed data, and p < 0.05 indicated a significant difference. Three samples were used for the tests.
RESULTS

Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images provide visual representations of the surface morphology for four different methods: (A) CDM (Cold-drying method), (B) FDM (Freeze-drying method), ODM (Oven-drying method) and (D) RTDM (room temperature drying method). These images allow us to observe and compare the unique features and structures of BC in each method at the microscale level.

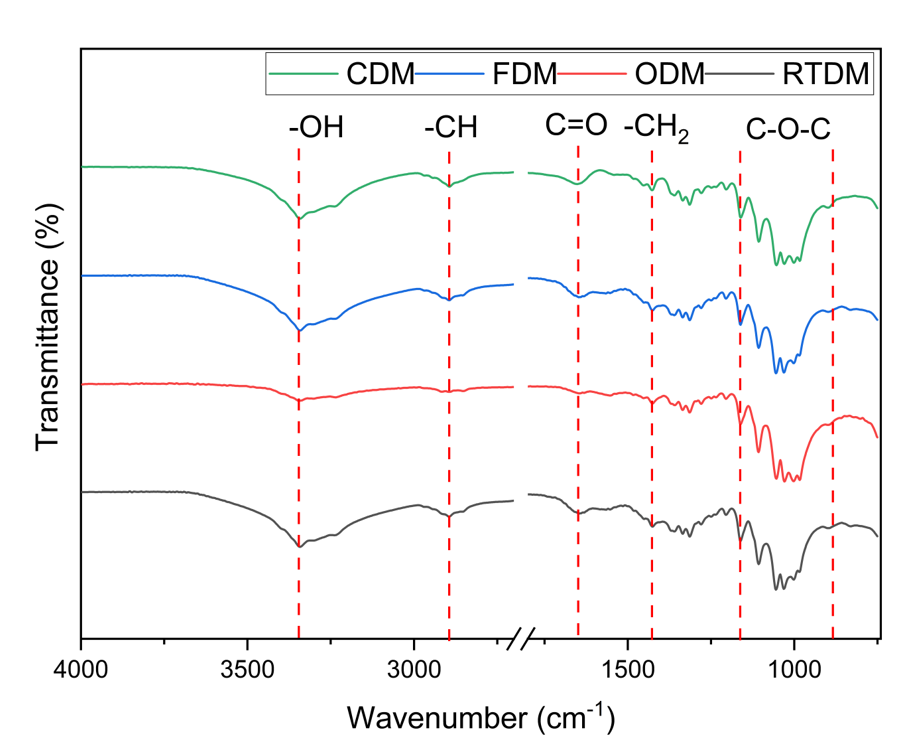
The Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy results reveal the unique effects of four distinct drying techniques on BC. These techniques are: (A) the Cold-drying method (CDM), (B) the Freeze-drying method (FDM); (C) the Oven-drying method (ODM); and (D) the Room Temperature Drying Method (RTDM). Examination of the FTIR spectra allows for the identification of variations in the functional groups within the structure of BC, corresponding to each drying method used

The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns yield insights into the influence of four different drying methods on the structure of BC. These methods are: (A) the Cold-drying method (CDM); (B) the Freeze-drying method (FDM); (C) the Oven-drying method (ODM); and (D) the Room Temperature Drying Method (RTDM). Analysis of the XRD patterns reveals variations in the crystallographic features of the BC, each associated with a specific drying method.

(A) The stress‒strain curves, (B) tensile strength, and (C) maximum elongation atbreak (%) of BC films obtained using four different drying methods. * indicates a significantdifference (P<0.05), whereas “ns” indicates no significant difference (P>0.05).

(A) Young’s modulus and (B) toughness of BC films were obtained using four different drying methods. * indicates a significant difference (P<0.05), whereas “ns” indicates no significant difference (P>0.05).
Physical properties (weight, thickness, water loss)
|
SAMPLE |
WEIGHT |
THICKNESS |
WATER LOSS (%) | ||
|
Wet (g) |
Dry (g) |
Wet (cm) |
Dry (cm) | ||
|
CDM |
69.0 ± 6.7 |
64.7 ± 7.7 |
14.9 ± 2.1 |
0.14 ± 0.01 |
94 ± 8* |
|
FDM |
60.8 ± 7.3 |
49.8 ± 7.9 |
15.3 ± 0.9 |
0.12 ± 0.03 |
96 ± 2* |
|
ODM |
67.8 ± 8.8 |
57.3 ± 8.5 |
15.3 ± 0.4 |
0.08 ± 0.01 |
94 ± 2* |
|
RTDM |
62.6 ± 9.4 |
48.7 ± 5.4 |
14.6 ± 0.9 |
0.12 ± 0.03 |
91 ± 2* |
Crystallinity of the dried bacterial cellulose membranes.
|
Sample |
Crystallinity (%) |
|
CDM |
59.95 |
|
ODM |
81.49 |
|
FDM |
59.09 |
|
RTDM |
69.56 |
However, the density of cellulose fibers produced by the CDM and ODM methods (Figure 1 (A, C)) reduces the number of holes between the fibers, and the thickening creates particle bundles on the surface. However, compared to the other samples, the fiber distribution is better organized, resulting in a more porous and hard bulk. A comparison of the BC sample dried at room temperature (RTDM) with that dried using FDM revealed that the former still maintained its hollow structure and that the latter increased the space between the fibers. Compared with RTDM, the FDM and CDM techniques are expected to have desirable fluid absorption capacities and preserve membrane porosity.
The FTIR spectra of the four drying methods, shown in Figure 2, show BC bands for stretching at approximately 3300–3400 cm, -CH stretching at approximately 2893 cm, and absorbed water at approximately 1649 cm5. The intensity of those peaks for three samples (CDM, FDM, and RTDM) indicates an increase in the number of -OH groups. It is assumed that there is no water vapor from the atmosphere that is transferred to BC and that, according to experimental studies, the process that transforms bound water into free water is reversible, but the process that transforms free water into evaporated water is irreversible. As stated in a study by Ana R. Rebelo et al., the main method of water loss is the evaporation of free water6. The free water molecules that reside on the surface of the membrane are the first to evaporate. The hydrogen bond between water and the BC membrane breaks at the same time because of the elevated temperature, releasing water molecules. The volume of water that evaporates increases as free water flows through the BC surface. Air saturation allows free water that has not evaporated to re-evaporate and become bound water, even though the binding constant rate is extremely low 6. The hydroxyl groups of the bound water could trap the holes in the valence band. Adsorbed water molecules or surface hydroxyl groups generate OH• radicals. The amount of water loss (%) in the FDM samples during the drying process was greater than that in the CDM, ODM, and RTDM samples. The reason for the differences between the intensity of the absorbed water peaks and the amount of water loss is that the high-temperature drying mechanisms allow water molecules to be easily removed and are unlikely to be converted into bound water. The dehydrated air process of the cold-drying system limited moisture in the water molecules released from the air. An increase in air flow caused more moisture to evaporate from the BC surface, which in turn caused the moisture to move from the BC center to the surface.
Peaks corresponding to –CH2 bending vibrations, –CH bending vibrations, OH in-plane bending, and COP stretching appear at wavenumbers of approximately 1431, 1367, 1334, and 1055 cm, respectively. Asymmetric and symmetric asymmetric stretching (C–O–C) are present at 1163 cm and 895 cm, respectively. The four drying methods (FDM, CDM, ODM, and RTDM) did not change the chemical structure of BC during the drying process.
The XRD patterns of the four drying techniques are shown in Figure 3. Three crystalline peaks at 14°, 16°, and 23° are attributed to the (1-10), (110), and (200) crystalline plates, respectively. Using Equation (2), the percentage of crystallinity was calculated. According to the XRD calculations,
The tensile strength and elongation under maximum stress were used to compare the mechanical characteristics of the four drying techniques, as shown inFigure 4. The RTDM had a tensile strength and elongation at a maximum stress of 2.47 ± 0.71 MPa and 22.67 ± 3.69%, respectively. Compared to the FDM and CDM samples, the RTDM samples exhibited a greater tensile strength. The higher crystallinity and dense fibrous network in the RTDM samples are the cause of this difference. Although the ODM samples have the highest percentage of crystallinity, an increase in temperature during the drying process can cause thermal degradation of BC, breakage of chemical bonds, and loss of structural integrity, resulting in the samples having the lowest tensile strength.
CDM films have greater elongation at maximum stress than do ODM, RTDM, and FDM films. CDM BC exhibited the typical behavior of resilient materials with high elongation under maximum stress and very little strain before fracture. The CDM prevented the loss of water because moisture was retained by the cold surface and thus prevented the nanocellulose fibers from breaking. The mechanism is the flow of air used in the drying process8. Consequently, compared to ODM and FDM, the films were demonstrated to elongate more prior to breaking. The tensile strengths of the RTDM film are also significantly greater than those of the three drying methods.
Compared to ODM, realignment may be limited by lower porosity and higher order (high crystallinity), resulting in lower tensile strength and strain. In contrast, an increase in tensile strength and deformation (Figure 4) in RTDM can be caused by strain hardening of the nanofibrous membrane caused by unraveling of the cellulose chains in the amorphous area and realignment of the fibers in the loading direction.
The calculation of Young's modulus, which is sometimes referred to as the modulus of elasticity, involves dividing the longitudinal stress by the strain. FDM BC showed less ductile behavior, with a low Young's modulus (Figure 5A) and a considerable maximum elongation at break before fracture (Figure 4). The tensile strength varies very little, although FDM exhibits low tensile strain, which may be related to larger pores (100–250 nm) being deformed compared to those of the other samples (Figure 1B).
Figure 5B shows that the toughness of the CDM and RTDM samples was greater than that of the ODM and FDM samples. The toughness was mathematically expressed as U = E/V, where V is the volume, U is the toughness, and E is the total energy from the start to fracture. It is also connected to the region under the stress‒strain curve that extends from the rupture point to the start of the deformation. The RTDM sample (535 ± 65 kJ/m) has a greater toughness than the CDM sample (343 ± 43 kJ/m), which means that the RTDM sample can be resilient. One of the characteristics of wound dressings is toughness, or the ability to withstand plastic deformation without breaking. Better wound protection is made possible by the structure in which wound dressings are formed during the drying process and are maintained without breaking under stress.
DISCUSSION
Research on BC characteristics, including surface morphology and physical-chemical properties, revealed that the drying techniques used had a significant impact. BC is naturally produced as a thin layer of hydrogel with more than 90% water content in its microfiber network9. This reveals the high porosity and capacity of the material to store water. However, the amount of water in the BC membrane needs to be partially removed to make it more suitable for making a membrane for gauze applications. ODMs are commonly used for water removal. However, during these processes, the original microporous structure of the material in the water-absorbing state significantly changes (Figure 1C) 10. Freeze drying is another membrane drying technique that helps to maintain the shape and porosity of fibers by preventing coagulation of microfibrils/microcrystals (Figure 1B) 11. In this approach, the water in BC first freezes and then decreases to be evacuated as vapor.
The relationships between the surface morphology, XRD data, and mechanical characteristics explain the trends observed for each drying method. The SEM image of the well-organized RTDM fibers (Figure 1D) demonstrates their exceptional mechanical characteristics. However, compared to other procedures, the RTDM approach yields a smaller amount of water that is eliminated, which requires a longer drying time and ideal sterilization conditions. Compared to those of the other two techniques, the SEM results show that CDM and FDM enable the preservation of the porous structure of BC. CDM, FDM, and RTDM preserve bound water molecules, while ODM completely removes free water molecules, disrupts hydrogen bonds, and reduces the number of surface OH groups. It follows that ODM is appropriate for preserving BC membranes. Unlike ODM, which has the highest crystallinity, ODM has the lowest elongation at break (19.56%), followed by RTDM and FDM (22.6% and 25.1%, respectively). CDM showed the highest elongation at break, approximately 34.38%, with high Young’s modulus and toughness values of 0.06 ± 0.004 MPa and 343 ± 43 kJ/m. It should be mentioned that because the appropriate tensile strength range for a wound dressing is 1 to 32 MPa, which is determined by the thickness of the human skin layer and satisfies the predetermined physical requirements at a largely adequate level, the deformation capacity must be greater than 30% 12.
CONCLUSIONS
From the results of the analysis, CDM BC was determined to be suitable for the production of wound dressing membranes because this method can remove more than 94% of the water while retaining optimal properties compared to other methods. In addition to maintaining the chemical structure of BC, BC has a low crystallinity (59%) and ideal mechanical properties, with a tensile strength of 1.4 MPa and a maximum elongation at break of 34.3%, which is suitable for making wound dressings.
LIIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED
BC: Bacterial cellulose
SEM: Scanning electron microscopy
XRD: X-ray diffraction
FTIR: Fourier transform infrared
CDM: Cold-drying method
ODM: Oven-drying method
FDM: Freeze-drying method
RTDM: Room-temperature drying method
COMPETITIVE INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was funded by the Ben Tre Department of Science and Technology under the grant under contract 1845/H-SKHCN.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
Thi Hiep Nguyen: conceptualization, project administration; Thi Thanh Tam Phan: writing – original draft, formal analysis, Tin Dai Luong: writing – original draft; Thao Nhi Dang Ngoc: writing – review and editing; Phuong-Thao Nguyen: data curation, visualization; Kieu Thi-Thuy Nguyen. All authors equally contributed to the final manuscript.

