An explicit topology optimization method using moving polygonal morphable voids (MPMVs)
- Mechanical Engineering Institute, Vietnam Maritime University, Hai Phong City, Viet Nam
Abstract
Introduction: Conventional topology optimization approaches are implemented in an implicit manner with a very large number of design variables, requiring large storage and computation costs. In this study, an explicit topology optimization approach is proposed by movonal morphable voids whose geometry parameters are considered as design variables.
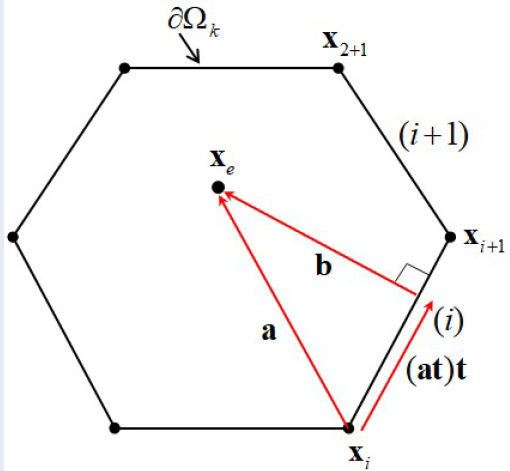
Methods: Each polygonal void plays as an empty-material zone that can move, change its shapes, and overlap with its neighbors in a design space. The geometry eters of MPMVs consisting of the coordinates of polygonal vertices are utilized to render the structure in the design domain in an element density field. The density function of the elements located inside polygonal voids is described by a smooth exponential function that allows utilizing gradient-based optimization solvers.
Results & Conclusion: Compared with conventional topology optimization approaches, the MPMV approach uses fewer design variables, ensure mesh-independence solution without filtering techniques or perimeter constraints. Several numerical examples are solved to validate the efficiency of the MPMV approach.

