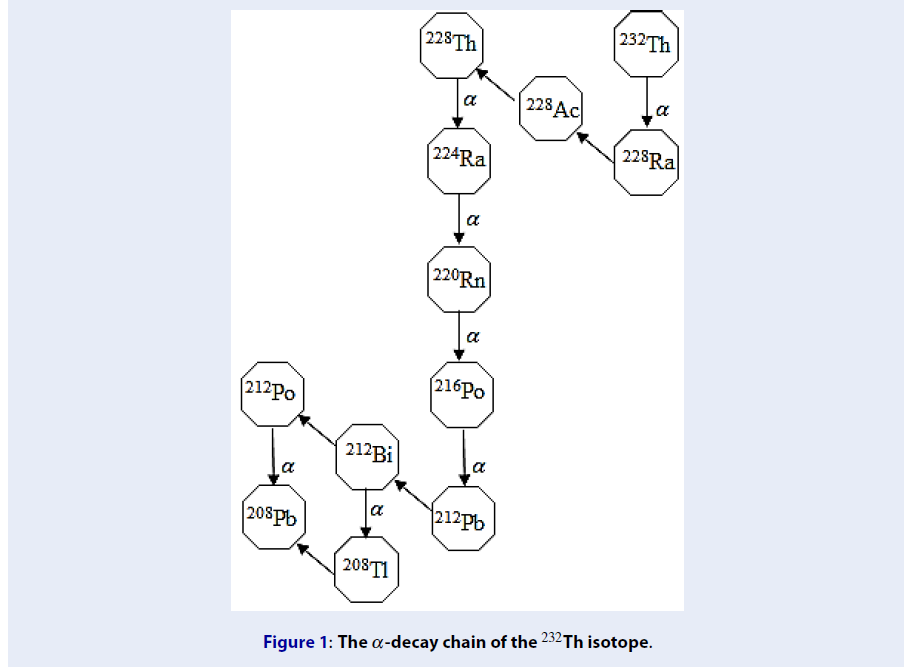
Critical concentration of the exotic nuclei in the 232Th chain for the alpha analysts
- Department of Physics, Sungkyunkwan University, South Korea
- Ho Chi Minh City University of Science, Vietnam
Abstract
The critical concentration plays an important role in the consideration of the analysts, such as gamma or alpha analyzers, for the isotopic analysis. Since the 232Th isotope and its a-decay daughters are abundant in the environments of soils, rocks and water, it is necessary to investigate the content of these isotopes to reduce the risks of health. In this work, the critical concentrations of the mentioned radioactive nuclei were estimated based on their radioactivities for the alpha analysts. The a-decay half-lives of the nuclei in the decay chain of the 232Th isotope were re-examined for the radioactivities. The semi-empirical formulae proposed by Viola-Seaberg, Royer and Poenaru were applied to the estimation. The predicted half-lives were normalized by their average values and compared to the data (NuDat) of the National Nuclear Data Center, Brookhaven National Laboratory. The results show that there exist a large uncertainty, 15% - 95% dispersed from the average values (in decimal logarithmic scale), of the half-lives evaluated by each models. Most of average half-lives are close to the NuDat data except the multi-decay-mode isotopes. The relationships between the estimated half-lives and the NuDat data are deduced as linear functions. The decay-constant deviations due to the half-life uncertainty are in the range of 1% - 120% from the average values. The large radioactivity uncertainty due to the half-lives estimated by the three models should be paid an attention for considering the environmental samples for the analysis of the natural exotic isotopes using alpha spectrometers. By assuming an efficiency of 100%, the critical concentration for the alpha analyst of the 232Th nucleus is found to be in the range 1.5 – 2.5 microgram/(l or kg).

