Chemical constituents of the ethyl acetate extract from the leaf of mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris L.)
- Faculty of Chemistry, University of Science, VNU-HCM
- aculty of Chemistry, University of Science, VNU-HCM
- Central Laboratory for Analysis, University of Science, VNU-HCM
Abstract
Introduction: Mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris L.) is a familiar herbal medicine and also a daily vegetable. It is one of the ingredients in the famous remedy "Cao ích mẫu" specializing in menstrual disorders or the omelet with mugwort that helps save blood flow to the brain to treat headaches. In both traditional medicine and the new drugs, diseases are usually treated by mugwort as diabetes, epilepsy combination for psychoneurosis, depression, irritability, insomnia, anxiety, and stress. To demonstrate the medicinal uses, the chemical constituents of this herbal were continually studied.
Methods: The leaves of mugwort were collected in Ba Ria - Vung Tau province, Vietnam. The plant was identified by the late pharmacist and botanist Binh Duc Phan. A voucher specimen (AV001) was deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Organic Chemistry, VNUHCM–University of Science. Dried leaf powder of A. vulgaris (11 kg) was extracted with methanol and evaporated under reduced pressure to give a methanol extract (910 g), which was dissolved in methanol-water (1:9) and then successively partitioned with petroleum ether, chloroform, and ethyl acetate. From the previously researched ethyl acetate fraction, nine compounds were isolated: six known phenolic compounds (luteolin, 6-methoxyluteolin, eupatilin, o-coumaric acid, vanillic acid, and protocatechuic acid), sinapyl alcohol diisovalerate, vulgarin, and one new compound (artanoic acid).
Results: In this research, ethyl acetate fraction was also studied. From subfraction EA4, six compounds were isolated by three skeletons: phenolic compounds (5,4′ -dihydroxyflavone and 4-hydroxyphenyl acetate), phenyl propanoid (methyl 2-O-b -D-glucopyranosylcoumarate and 2-O-b -D-glucopyranosylcoumaric acid) and uracil (5-methyluracil and uridine). The structure of the isolated compounds was determined to base on 1D, 2D NMR spectra, HR-ESI-MS, and comparison with published data.
Conclusion: Particularly, four compounds (methyl 2-O-b -D-glucopyranosylcoumarate, 2-O-b -D-glucopyranosylcoumaric acid, 5-methyluracil, and uridine) were known for the first time from this species.
INTRODUCTION
L., a familiar herbal species in Viet Nam, is used in both traditional medicine and new drugs. Diseases are usually treated by mugwort as diabetes, epilepsy combination for psychoneurosis, depression, irritability, insomnia, anxiety, and stress 1. The primary responsibility for these activities are constituents, such as flavonoids, coumarins, sesquiterpene lactones, volatile oils, inulin, and traces of alkaloids 2. In the previous research of my group, three flavonoids (luteolin, 6-methoxyluteolin, and eupatilin), four phenolic compounds (o-coumaric acid, vanillic acid, protocatechuic acid, and sinapyl alcohol diisovalerate), and two sesquiterpene lactones (vulgarin and artanoic acid) are isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction3.
In this study, the ethyl acetate fraction is continuously researched and six compounds are isolated, including methyl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylcoumarate (1), 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylcoumaric acid (2), 5-methyluracil (3), uridine (4), 5,4′-dihydroxyflavone (5), and 4-hydroxyphenyl acetate (6).
METHOD
General experimental procedures
The NMR spectra were acquired on a Bruker Avance III 500 MHz spectrometer with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard, with chemical shifts expressed in (ppm) values. The HR-ESI-MS were determined with a MicrOTOF QII mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics). Analytical and preparative thin-layer chromatography (TLC) were performed on precoated Merck Kieselgel 60 F or RP-18 F plates (0.25 mm or 0.5 mm thickness).
Plant material
The leaves of L. were collected at Lang Dai, Dat Do, Ba Ria - Vung Tau province, Vietnam on May 2011. The plant was identified by the late pharmacist and botanist Binh Duc Phan. A voucher specimen (AV001) was deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Organic Chemistry, VNUHCM–University of Science.
Extraction and isolation
From the ethyl acetate fraction in the previous research3, fraction EA4 (6.14 g) was subjected to silica gel column chromatography eluting with petroleum ether –ethyl acetate, followed by ethyl acetate –methanol with increasing polarity to yield six fractions (EA4.1 – 6). Fraction EA4.3 (300.6 mg) was separated over a silica gel column eluted with chloroform-methanol (from 9.5:0.5 to 0:10), as well as preparative TLC, eluted with petroleum ether–acetone (4:6) to afford 1 (6.0 mg), 2 (5.5 mg), and 6 (8.2 mg). Fraction EA4.4 (207.5 mg) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with methanol, and further fractionated by silica gel column chromatography eluted with chloroform– ethyl acetate (from 9:1 to 3:7) to obtain 3 (6.3 mg), 4 (4.0 mg), and 5 (4.5 mg).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Six compounds (1 – 6) were isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction of the leaves of L.
Compound 1 was obtained as a white amorphous powder, and its molecular formula was determined as CHO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 341.1161 [M+H]. The H-NMR spectrum of 1 showed four signals of four aromatic protons at 7.02 (1H, , 7.5, 7.5 Hz, H-5), 7.19 (1H, , 8.5 Hz, H-3), 7.37 (1H, , 8.5, 7.5, 1.5 Hz, H-4), 7.71 (1H, , 7.5, 1.5 Hz, H-6). Furthermore, the C-NMR and HSQC spectra showed aromatic carbon signals at 115.5 (C-3), 122.3 (C-5), 128.7 (C-6), 132.1 (C-4), and two signals of quartet carbon at 123.4 (C-1), 156.1 (C-2). It demonstrated that 1 had a 1,2-di substituted benzene. There were two signals of two olefin protons, (E) configuration, at 7.95 (1H, , 16.0 Hz, H-7), and 6.64 (1H, , 16.5 Hz, H-8) with carbon signals at 139.8 (C-7), 118.7 (C-8); and a carboxyl group at 167.3 (C-9). HMBC correlations between H-7/C-2, C-8, C-9; H-8/C-9 showed that 1 had the 2-h ydroxycinnamoyl skeleton. The signals of a methoxy group at 3.70 (3H, , H-10) and 51.7 (C-10), correlated with C-9 in the HMBC spectrum (Figure 1). Therefore, the methoxy group linked to the carboxyl group of the cinnamoyl skeleton.

Significant HMBC (→) correlations of 2-hydroxycinnamoyl skeleton.
H-NMR and C-NMR spectra showed an anomer proton at 5.00 (1H, , 8.5 Hz, H-1′) and 100.4 (C-1′). The HMBC correlation between H-1′/C-2, C-3′ showed that the sugar moiety linked to cinnamoyl skeleton at C-2.
The above data compared with the published one indicated that 1 was methyl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylcoumarate4.
Compound 2 was obtained as a white amorphous powder, and its molecular formula was determined as CHO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 326.1033 [M], calcd 326.1002. The H-NMR, C-NMR spectra of 2 were similar to those of compound 1. However, the lack of the methoxy group in compound2 showed that it was a carboxylic acid. The comparison of the above data with the one in the literature5 assigned 2 as -coumarico glucosidase acid.
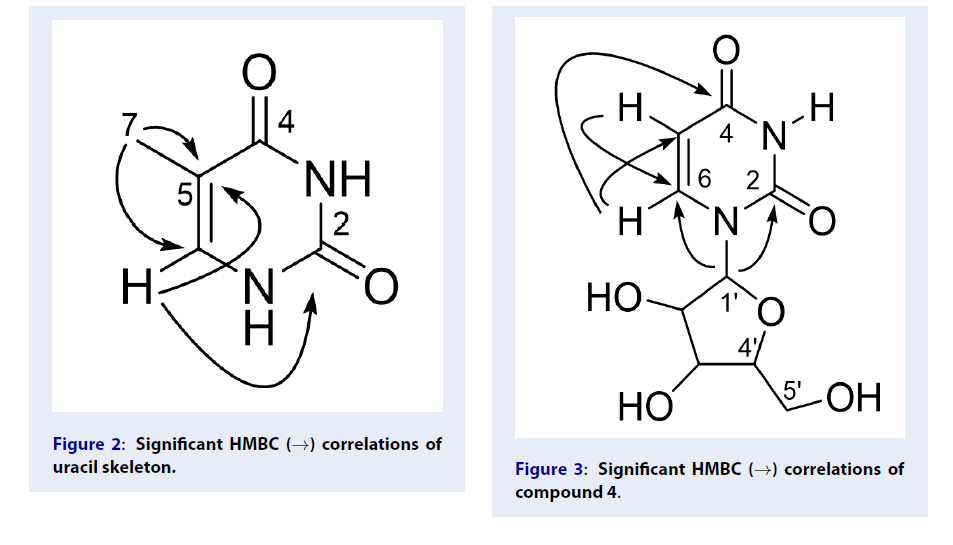
Compound 3 was obtained as a white amorphous powder and its molecular formula was determined as CHNO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 127.0451 [M+H]. The H-NMR spectrum displayed four signals including two amide protons at 10.56 (r), and 10.97 (r), a methyl group at 1.71 (3H, , 1.0 Hz, H-7), and an olefin proton signal at 7.23 (1H, ). The C-NMR and HSQC spectra showed two signals of two carbonyl carbons at 165.2 (C-2) and 151.7 (C-4), two olefin signals at 108.2 (C-5) and 138.2 (C-6) and a methyl group at 12.2 (C-7). The above information showed an uracil skeleton in compound3. The HMBC correlations between H-7/C-5, C-6 confirmed the position of the methyl group on the C-5 of the uracil skeleton (Figure 2).

Significant HMBC (→) correlations of uracil skeleton.
Based on the above discussions and the comparison with the published ones5, the structure of 3 was 5-methyluracil.
Compound 4 was obtained as a white amorphous powder and its molecular formula was determined as CHNO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 267.0628 [M+Na] and 245.0825 [M+H].H-NMR, C -NMR, HSQC spectra showed that compound 4 had the uracil skeleton as in compound3. The H-NMR spectrum showed an amide proton at 11.29 (r), two olefin protons with the (Z) configuration at 7.88 (1H, , 8.0 Hz, H-6), 5.64 (1H, , 8.0 Hz, H-5). The C-NMR spectrum showed two olefin carbons at 102.2 (C-5) and 141.2 (C-6); two carbonyl groups at 163.6 (C-2) and 151.2 (C-4).
In addition, there was an anomer proton at 5.77 (1H, , 5.5 Hz, H-1′) and five oxymethine proton of a sugar moiety at 3.53–5.36 in the H-NMR spectrum. The C-NMR spectrum showed an anomer carbon at 88.1 (C-1′), and four oxynated carbons at 85.4 (C-4 ′), 73.8 (C-2 ′), 70.3 (C-3 ′) and 61.2 (C-5 ′). It demonstrated a sugar moiety in compound 4.
The HMBC correlations between proton H-6/C-2, C-4, C-5 and C-1′, proton H-5/C-2, C-6, C-1′, and the anomer proton H-1′/C-2, C-5, C-6, C-2′, C-3′, C-4′ showed that the sugar moiety linked to the first nitrogen of the uracil skeleton (Figure 3).

Significant HMBC (→) correlations of compound 4.
The above data compared with the published one indicated that 4 was uridine6.
Compound 5 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder and its molecular formula was determined as CHO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 254.0593 [M], calcd 254.0579. The H-NMR spectrum displayed two signals of four aromatic protons of a 1,4-disubstituted benzene at 7.91 (2 H, , 8.5 Hz, H-2′ and H-6′) and 6.91 Hz (2H, = 8.5 Hz, H-3′ and H-5′). Moreover, there were three signals of three aromatic protons of a 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzene at 7.32 (1H, , = 2.5 Hz, H-8); 7.53 (2H, = 7.5 Hz, H-6 and H-7) and an olefin proton at 7.08 (1H, , = 2.5 Hz, H-3). The C-NMR spectrum showed fifteen carbons: seven aromatic quaternary carbons (δ 182.9, 167.4, 162.4, 158.3, 149.8, 120.7, 109.9), eight aromatic methine carbons (δ 115.9 (C-3′, C-5′), 132.7 (C-2′, C-6′), 110.8, 130.2, 107.1 and 102.5). Based on the above discussions and the comparison with the published one7, the structure of 5 was 5,4 ′ -dihydroxyflavone.
Compound 6 was obtained as a white amorphous powder, and its molecular formula was determined as CHO by HR-ESI-MS analysis at 175.0377 [M+Na], calcd 175.0371. The H-NMR spectrum showed two signals of four aromatic protons of a 1,4-disubstituted benzene at 7.44 (2H, = 9.0 Hz) and 6.74 (2H, = 9.0 Hz), one methyl group atδ 2.01 (3H, ), and one hydroxyl at 8.93 (1H, ). The C-NMR spectrum showed four signals of six aromatic carbons (δ 154.2, 121.7, 121.6, 115.8), one methyl group (δ 24.0), and one carboxyl group (δ 171.4). On the basis of the above discussions and the comparison with the published one8, the structure of 6 was 4-hydroxyphenyl acetate.
CONCLUSION
From the leaves of L. collected at Ba Ria - Vung Tau province, six compounds were isolated, including methyl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylcoumarate (1), 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosylcoumaric acid (2), 5-methyluracil (3), uridine (4), 5,4′-dihydroxyflavone (5), and 4-hydroxyphenyl acetate (6). Compounds 1, 2, 3, 4 were known for the first time from this species.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
1D NMR: One-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance;
2D NMR: Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance;
C-NMR: Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance;
H-NMR: Proton nuclear magnetic resonance;
HR-ESI-MS: High-resolution electrospray ionization mass;
TMS: Tetramethylsilane;
TLC: Thin-layer chromatography;
EA: Ethyl acetate;
HMBC: Heteronuclear Multiple Quantum Coherence.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
Truong Van Nguyen Thien, Thien Tai Phan, Tung Thanh Phan, Kim Lien Tran Thi, Nhu Tiet Thi Tran, and Phu Hoang Dang have contributed in conducting experiments, getting hold of data and writing the manuscript.
Linh Phi Nguyen, Quang Ton That have contributed significantly explanation of data and revising the manuscript.

