A comparative study on thermoelectric properties of ZnO bulks and thin films
- Center for Innovative Materials and Architectures (INOMAR), HoChiMinh City, Vietnam
- Laboratory of Advanced Materials, University of Science, HoChiMinh City, Vietnam
- Faculty of Materials Science and Technology, University of Science, HoChiMinh City, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: Zinc oxide (ZnO) is well-known as a promising thermoelectric material owing to its safety, inexpensiveness, and thermal stability. This research provides an overview of thermoelectric potentials, including structure, electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor of pure ZnO semiconductor synthesized in bulk and thin-film forms.
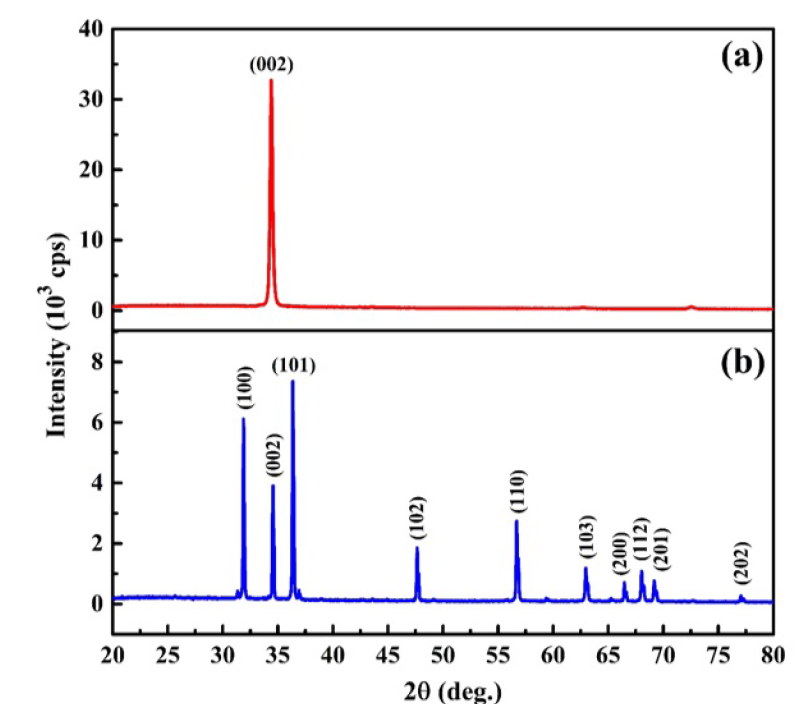
Methods: The ZnO bulk was synthesized by solid-state reaction at high temperature, while the thin film was prepared by d.c. magnetron sputtering technique. The temperature-dependent thermoelectric properties of all the samples were measured by the Seebeck LSR-3 system. The crystallographic and surface morphological information of the samples were obtained by using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), respectively.
Results: The XRD results confirm that both the bulk and thin-film have polycrystalline structure and characteristics of hexagonal-wurtzite ZnO. Through the FESEM observation, the bulk is well densified under high-temperature condition, while the thin-film achieve good orientation and close-packed grains. At 573 K, the obtained thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor) are respectively 352.4 S/cm, -89.5 µV/K and 282.5 µW/mK2 for the ZnO bulk; and 289 S/cm, -113.8 µV/K and 374.3 µW/mK2 for the ZnO film.
Conclusion: The comparative study shows the good thermoelectric potential of ZnO material in both forms of bulk and thin film. Among them, the thin film has better results, especially in the Seebeck coefficient and power factor than one.

