Isolation, Characterization, and Simultaneous Quantification of Main Chemical Constituents from Cassia Alata Linn. Leaves
- Center for Research and Technology Transfer, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Vietnam
Abstract
The leaves of Cassia alata L. are used in traditional Vietnamese medicine to treat ringworm and fungal skin infection. This study aimed to isolate marker compounds from the crude methanol extract of C. alata leaves and develop a validated method to control these compounds using HPLC-DAD. The three isolated compounds were identified as rhein (1), aloe-emodin (2), and kaempferol (3) by NMR and HR-ESI-MS. A quick, precise, and accurate HPLC-DAD method in 20 min of analysis time to quantify isolated maker compounds of Cassia alata was developed for the first time. The analysis was performed on a Hypersil GOLD C18 column (150 x 2.1 mm, 3 µm) with 0.1% formic acid in water-methanol gradient elution. The linearity, specificity, sensitivity, precision, and accuracy parameters were validated. The accuracies of the method were 99.0 – 103.5% and linearity (r2 > 0.9995) were achieved. The LODs and LOQs were less than 0.74 µg/mL and 2.25 µg/mL. The developed HPLC method could be applied for quality control testing of C. alata leaves. Keywords: Cassia alata L., kaempferol, rhein, aloe-emodin, HPLC-DAD.
INTRODUCTION
(L.) Roxb. () belongs to the Fabaceae family that is distributed widely in tropical regions such as tropical Africa, tropical Asia, Australia, Mexico, and Pacific Islands. In Vietnam, it grows mainly in the lowland mountain region: Binh Duong, Lam Dong, Binh Dinh, Phu Yen, Khanh Hoa, Quang Ngai, Quang Nam, and Ha Tinh. The leaves of have been traditionally used as a Vietnamese medicine for the effective treatment against ringworm and other skin diseases such as tinea imbricata, skin rash, and herpes zoster.1 The leaves and flowers of are also used to treat constipation, hepatalgia, and laxative due to active anthraquinones.2 In the recent literature review of Hennebelle (2009), leaves have been reported to possess many pharmacological activities including antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and analgesic activities.3 Several studies reported that leaves contain mainly anthraquinones, and flavonoids, which play important roles in biological activities.4, 5
Although the leaves of have multiple medicinal uses, only a few researches on the bioactivities of crude extracts and chemical constituents in the leaves of from Vietnam.6, 7, 8, 9 The objectives of the present study were to isolate maker compounds from the methanol extract of leaves due to the unavailable reference compounds and establish an analytical method for quantification of these compounds, which was very helpful in the quality control of leaves in the herbal market.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
General instruments and chemical
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance III spectrometer (500 MHz for H and 126 MHz for C). High resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (HR-ESI-MS) data were recorded on SCIEX X500R QTOF high-resolution mass spectrometer system. Pure compounds were separated by an open column and CombiFlash Rf 200 (Isco Teledyne).
Methanol and formic acid (HPLC-grade) were purchased from Scharlau (Sentmenat, Spain). Deionized water was made by Millipore Milli-Q Plus system (Millipore, USA) used for HPLC. Rhein, aloe-emodin, and kaempferol were from NatPro (Vietnam).
Plant material
L. leaves were collected in An Giang, Vietnam, in January 2019 and identified by botanist Tran Huu Dang MSc, Institute of Ecology, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology. A voucher specimen (Code: NaPro.33.0119) was deposited in the Center for Research and Technology Transfer, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology. The plant material was washed with water, dried at 60C in an oven, and then ground into a fine powder by an electric blender.
Extraction and isolation
The powdered leave material (2.0 kg) was macerated with MeOH at room temperature for 48 hours. The methanolic solution was filtrated through filter papers. The filtrate was then concentrated to obtain 225 g of the crude extract by rotary vacuum evaporation. This crude extract was sequentially partitioned with n-hexane, EtOAc, and the remaining part. Respective solutions were concentrated using a rotary evaporator to give 88, 26, and 95 g of dry extracts. The mixture of EtOAc extract and MeOH extract (121 g) was applied onto a column chromatography over silica gel 60 (70-230 mesh). The column was eluted by increasing the polarity of the mobile phase from n-hexane to EtOAc (100:0 → 0:100) to obtain four major fractions (F1-F4). F2 and F3 were fractionated and purified by MPLC over silica gel 60 (70-230 mesh) with a flow rate 10 mL/min, mobile phase CHCl-MeOH (95:5). Compound 1 (121 mg) was obtained from F3 eluted with n-hexane-EtOAc (50:50) by recrystallization from MeOH. Compounds 2 (28 mg) and 3 (48 mg) were isolated from F2 eluted with n-hexane-EtOAc (75:25) by medium pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC) over silica gel 60 (230-400 mesh) and recrystallization. All three compounds 1, 2, and 3 were identified by direct comparison with TLC using the mobile phase of chloroform-methanol (9:1 v/v); by the spectroscopic studies of H-NMR, C-NMR, and mass spectra; and by comparison with published data from the literature.
Quantitative HPLC-DAD analysis
Preparation of the standard stock solution and samples
Separate stock solutions of standard compounds were prepared in methanol (500 μg/mL). A combined methanol stock solution containing three standards was then diluted to provide a series of concentrations (within the range from 1-100 μg/mL) for method validation analysis. The extract samples were prepared by weighing 100 mg of the sample accurately and adjusting to 25 mL in methanol. All sample solutions were filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter before use.
HPLC condition
Chromatographic analyses were carried out on a Thermo Scientific Dionex Ultimate 3000 UHPLC systems (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., MA, USA) equipped with Ultimate 3000 Rapid Separation (RS) quaternary pump WPS-3000RS autosampler, Ultimate TCC-3000RS column thermostat, and DAD-3000RS diode array detector, Chromeleon CDS 7.2 software. The chromatographic separation was carried out on a Hypersil GOLD C18 column (150 x 2.1 mm, i.d. 3 µm). The mobile phases were (A) 0.1% formic acid in water and (B) methanol. Gradient elution was used: linear gradient from 10 to 25% B in A for 4 min; 25 to 45% B in A for 1 min; 45 to 80% B in A for 10 min; 80 to 100% B in A for 0.5 min; 100% B for 5 min. The flow rate was 0.40 mL/min at 25 ± 1C. The detection wavelength was at 254 nm and the injection volume was 2 μl for all samples and standards.
Validation of HPLC method
The developed method was validated in terms of specificity, linearity, the limit of detection (LOD), the limit of quantification (LOQ), precision, and accuracy according to requirements of the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines. The specificity was validated by analysis of the standard, blank, sample, and spiked sample to show interferences unaffected to the standards of interest. The linearity was determined using a mixed standard solution at five concentrations. Calibration curves were generated by linear regression plotting the peak areas against concentrations with a correlation coefficient (r) > 0.9995. The LOD and LOQ were calculated according to the formula LOD = 3.3σ/a and LOQ = 10σ/a, where a is the slope of the calibration curve, and σ is the standard deviation of response. The accuracy was evaluated by adding known quantities of standard solution into the pre-analyzed sample in triplicate with the ratio of 80%, 100%, 120% of each target compound presented in the sample. The percent recovery was calculated using the following formula: Recovery (%) = (amount of spiked sample – the amount of unspiked sample) /amount of added standard x 100%. The precision was determined by analyzing six replicates of one sample solution continuously. The results were expressed using the relative standard deviation (% RSD), which should be lower than 5% to be accepted.
RESULTS
Structure elucidation of isolated compounds
Three compounds were successfully isolated from the leaves of . The melting point of isolated compounds was measured by Electrothermal IA9200 (Cole-Parmer, UK)
Compound 1: Yellow powder, melting point (m.p.) 285-287C, TLC Rf: 0.18 (The eluted solvent system was CHCL: MEOH (9:1)), HR-ESI-MS : 283.0239 [M-H] (calcd. for CHO – H, 283.0243). H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d): δ 13.79 (1H, s, -COOH), 11.89 (2H, s, 1-OH, 8-OH), 8.12 (1H, d, J = 1.5 Hz, H-4), 7.83 (1H, t, H-6), 7.75 (1H, d, J = 1.5 Hz, H-2), 7.73 (1H, dd, J = 7.5, 0.5 Hz, H-5), 7.41 (1H, dd, J = 8.4, 0.9 Hz, H-7). C-NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d): δ 191.47 (C-9), 181.26 (C-10), 165.68 (COOH), 161.60 (C-1), 161.27 (C-8), 138.34 (C-3), 137.84 (C-6), 133.99 (C-14), 133.38 (C-11), 124.85 (C-7), 124.37 (C-2), 119.68 (C-5), 118.99 (C-4), 118.87 (C-13), 116.33 (C-12).
Compound 2: Light yellow powder, m.p. 223-224C, TLC Rf: 0.7 (The eluted solvent system was CHCL: MEOH (9:1)), HPLC Rt: 9.90 min, HR-ESI-MS : 269.0452 [M-H] (calcd. for CHO – H, 269.0450). H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d): δ 11.68 (2H, s, 1-OH, 8-OH), 7.80 (1H, t-like, J = 7.9 Hz, H-6), 7.71 (1H, d, J = 7.1 Hz, H-5), 7.68 (1H, s, H-4), 7.37 (1H, d, J = 8.3 Hz, H-7), 7.29 (1H, s, H-2), 5.58 (1H, s, -CH-OH), 4.63 (2H, s, -CH). C-NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d): 191.67 (C-9), 181.55 (C-10), 161.69 (C-1), 161.40 (C-8), 153.74 (C-3), 137.40 (C-6), 133.39 (C-11), 133.18 (C-14), 124.48 (C-7), 120.77 (C-2), 119.41 (C-5), 117.16 (C-4), 115.95 (C-12), 62.13 (CH).
Compound 3: Yellow amorphous power, m.p. 322-324C, TLC Rf: 0.53 (The eluted solvent system was CHCL: MEOH (9:1)), HPLC Rt: 5.85 min, HR-ESI-MS : 285.0402 [M-H] (calcd. for CHO – H, 285.0399). H-NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d): δ 12.48 (1H, s, 5-OH), 8.07 – 8.03 (2H, m, H-2’/H-6’), 6.95 – 6.92 (2H, m, H-3’/H5’), 6.44 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-8), 6.42 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-6). C-NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d) δ 175.89 (C-4), 163.88 (C-7), 160.70 (C-5), 159.18 (C-4’), 156.17 (C-9), 146.82 (C-2), 135.63 (C-3), 129.48 (C-2’/C-6’), 121.66 (C-1’), 115.42 (C-3’/C-5’), 103.03 (C-10), 98.19 (C-6), 93.46 (C-8).
Optimization of HPLC conditions
The HPLC conditions were optimized using the crude methanol extract (CE) with different mobile phases and an elution gradient program. The peak separation was obtained better with the mobile phase consisted of methanol-water in comparison with acetonitrile-water. Moreover, 0.1% formic acid (v/v) was added to improve the peak tailing and symmetry. The proposed mobile phase containing methanol-0.1% formic acid in water gave the optimum chromatographic separation of marker compounds (Figure 2). The elution program was described in the HPLC condition section (2.4.2) within 20 min. The detection wavelength at 254 nm was selected for quantitative analysis of the target components because all compounds have strong UV absorption at this wavelength.
HPLC method validation
As shown in
System suitability parameters of CE sample
|
Parameters |
Rhein |
Aloe-emodin |
Kaempferol | |||
|
Rt |
Mean |
RSD (%) |
Mean |
RSD (%) |
Mean |
RSD (%) |
|
N |
14.92 |
0.41 |
13.49 |
0.35 |
11.35 |
0.43 |
|
T |
200757 |
0.33 |
173356 |
0.29 |
159434 |
0.38 |
|
Rs |
1.06 |
0.59 |
1.17 |
0.79 |
1.12 |
0.87 |
|
k’ |
3.57 |
1.21 |
10.91 |
1.03 |
17.66 |
0.89 |
|
Rt |
12.82 |
0.88 |
11.49 |
0.78 |
9.51 |
0.93 |
Application method
The validated HPLC-DAD method was applied for qualitative determination of the three standard compounds in four extract samples of leaves, including crude methanol extract (CE), hexane extract (HE), ethyl acetate extract (EE), and methanol extract (ME). The amount of the 3 standard compounds were calculated (
DISCUSSION
Based on spectral analysis and comparison to the literature8, 10, compounds 1, 2, and 3 were elucidated to be rhein, aloe-emodin, and kaempferol, respectively. The purities of isolated compounds were more than 98% determined by HPLC-DAD. The structures of these constituents are shown in Figure 1.
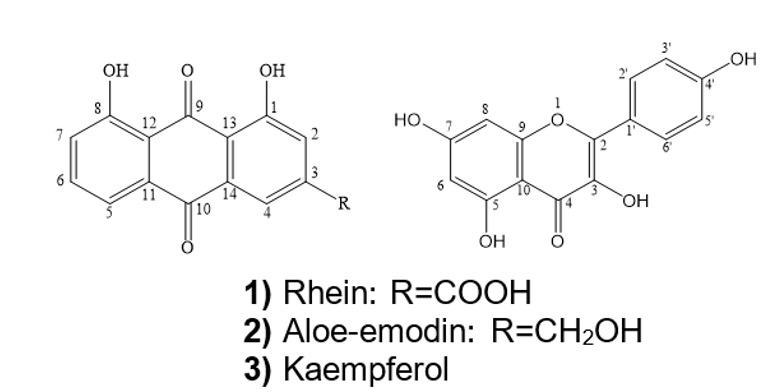
Structures of the compounds 1-3.
The pharmacological effects of these compounds have been reported in several studies. Kaempferol denotes many bioactivities, including antitumor, antioxidant, antidiabetic, etc., while rhein and aloe-emodin possess hepatoprotective activity in rats, antifungal, nephroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities.10, 11, 12, 13 All three markers show strong inhibitory effects against bacteria and fungi, including S. aureus, S. typhi, Trichophyton rubrum, and Epidermophyton floccosum,3 explaining the traditional use of C. alata leaves in the skin diseases treatment. Therefore, these predominant active constituents were used as marker compounds for quality control of C. alata leaves in the herbal market. The quantitative analysis of multiple pharmacological compounds was selected because of this widely practiced approach for the determination of active components in a medicinal plant.

HPLC chromatogram of specificity test. (A. Sample; B. Blank; C: Spiked sample; D: Standard; 1. Kaempferol; 2: Aloe-emodin; 3: Rhein)
The high specificity was performed by no detection of interferences at the retention time of standard compounds in the chromatogram of the reagent blank. Furthermore, the chromatogram of sample spiked standard showed higher signal intensities than its sample (Figure 2). The calibration curves were obtained using mixed standard solutions at five concentrations in the test range of 1 – 100 μg/mL. The linear regression analysis showed excellent correlation coefficients (r>0.9995). The LOD and LOQ values were found in the range of 0.51 – 0.74 and 1.54 – 2.25 µg/mL, respectively. This result demonstrated the highly sensitivity of the developed method to qualify and quantify the maker components' content. The linearity, LODs, and LOQs of standard analytes are summarized in
Recovery test (n=9)
|
Analytes |
Spiked (µg) |
Recorded (µg) |
Recovery (%) |
RSD (%) |
|
Kaempferol |
37.03 47.55 58.06 |
85.03 94.85 104.68 |
103.51 101.26 99.86 |
1.67 1.23 0.78 |
|
Aloe-emodin |
19.21 19.78 21.21 |
8.23 9.07 13.12 |
102.24 99.05 102.24 |
2.03 1.51 0.84 |
|
Rhein |
15.19 17.41 18.98 |
6.67 8.81 10.46 |
99.27 100.35 99.53 |
1.46 2.18 1.81 |
Calibration curves, LODs and LOQs of standard compounds
|
Analytes |
Regression equation (y = ax + b) |
r2 (n=6) |
Linear range (µg/ml) |
Sensitivity |
Precision | ||
|
LOD (µg/ml) |
LOQ (µg/ml) |
Mean |
RSD (%) | ||||
|
Rhein |
y = 0.25281x + 0.12276 |
0.99970 |
1-100 |
0.51 |
1.54 |
11.80 |
0.46 |
|
Aloe-emodin |
y = 0.27887x + 0.01927 |
0.99986 |
1-100 |
0.61 |
1.86 |
3.35 |
1.55 |
|
Kaempferol |
y = 0.24225x + 0.01074 |
0.99981 |
1-100 |
0.74 |
2.25 |
2.43 |
1.60 |
Content of three compounds in different extracts (mg/g)
|
Sample |
Contents (mg/g, n=3) | ||
|
Rhein |
Aloe-emodin |
Kaempferol | |
|
CE |
3.92 ± 0.02 |
4.94 ± 0.01 |
21.39 ± 0.02 |
|
HE |
1.63 ± 0.03 |
3.71 ± 0.01 |
5.95 ± 0.05 |
|
EE |
18.84 ± 0.02 |
32.85 ± 0.03 |
210.35 ± 0.03 |
|
ME |
3.82 ± 0.04 |
2.84 ± 0.01 |
2.71 ± 0.02 |
The quantification results showed that the highest content of rhein, aloe-emodin, and kaempferol was presented in ethyl acetate extract compared with other solvent extracts.
CONCLUSION
In this study, a validated HPLC-DAD method was established to detect and quantify three isolated marker components, including rhein, aloe-emodin, and kaemferol from leaves. The isolation and characterization of these marker constituents were also described, which is the prerequisite for quality control of leaves because of commercial unavailability.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
calcd. MW: calculated molecular weight.
CHCl: Chloroform.
DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
EtOAc: Ethyl acetate.
HPLC-DAD: High-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection.
HR-ESI-MS: High resolution - Electrospray ionization - Mass spectroscopy.
ICH: International Conference on Harmonisation.
LOD: Limit of detection.
LOQ: Limit of quantitation.
m.p.: Melting point.
MeOH: Methanol.
MPLC: Medium pressure liquid chromatography.
NMR: Nuclear magnetic resonance.
Rf: Retention factor.
TLC: Thin layer chromatography.
UHPLC: Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors contributions
Xxx
Acknowlegdements
Xxx if any

