Structural, electrical and thermoelectric characterizations of bismuth-doped ZnO ceramic material
- Laboratory of Advanced Materials, University of Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Faculty of Physics and Engineering Physics, University of Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Center for Innovative Materials and Architecture (INOMAR), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: ZnO is a potential semiconductor material for thermoelectric (TE) applications at high temperature. In this study, doping Bi atoms aims to improve the power factor of ZnO ceramic. Based on the analyses of structural and TE properties, the enhancement in Seebeck coefficient proves the benefit of Bi doping.
Methods: The ZnO and Bi-doped ZnO (BZO) ceramics were fabricated by solid-state reaction at 1400oC in air. The Seebeck LSR-3 system measured both samples’ TE properties, with a combined Hall effect at room temperature. The crystalline structure was analyzed through the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique.
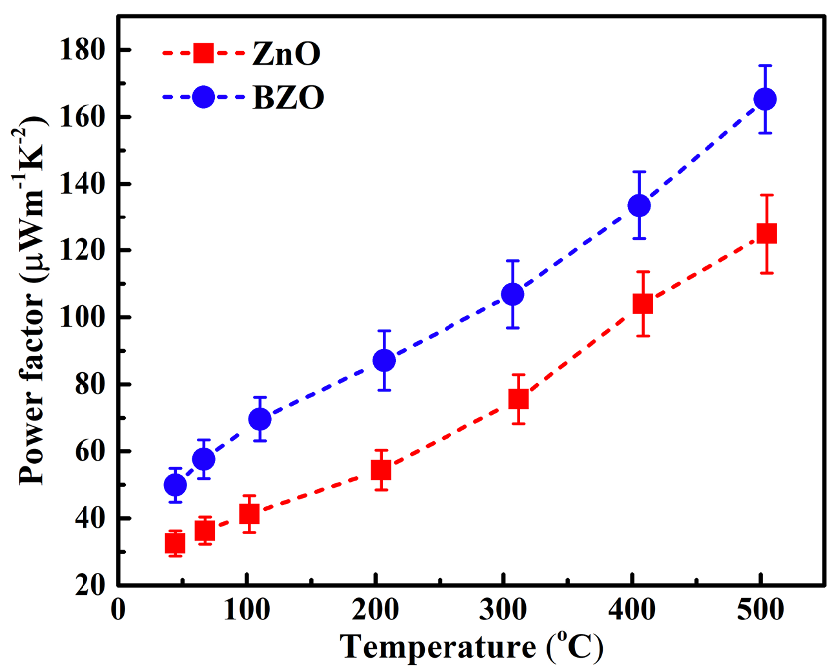
Results: The XRD patterns show all samples having polycrystalline hexagonal wurtzite structure. Although the crystallinity is enhanced, Bi doping reduces significantly carrier concentration from 3.4×1019 to 1.1×1019 cm-3 at room temperature. As a result at 500oC, the electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor are 126 Scm-1, -99 µVK-1, and 124 µWm-1K-2 for pure ZnO; and 76 Scm-1, -142 µVK-1, and 165 µWm-1K-2 for BZO ceramic, respectively.
Conclusion: The power factor of Bi-doped ZnO is improved by 32% as compared to pure ZnO at 500oC. The raise of Seebeck coefficient is the main reason for the growth of power factor.

