Optimization of the optical properties of circular lattice As2Se3 photonic crystal fibers over a wide range of wavelengths
- University of Education, Hue University, 34 Le Loi, Hue City, Viet Nam
- Department of Physics, Vinh University, 182 Le Duan, Vinh City, Viet Nam
Abstract
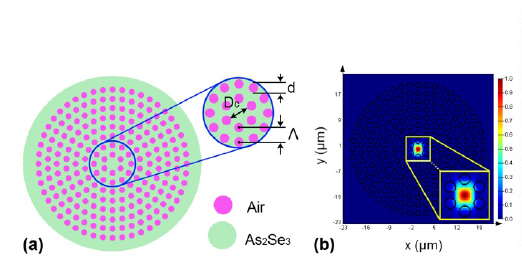
In this paper, the dispersion and nonlinear properties of circular lattice photonic crystal fibers with As2Se3 substrates are investigated over a wide wavelength range up to 11 µm. By solving Maxwell's wave equations using the full-vector finite-difference eigenmode method, the optical properties of the PCFs have been analyzed in detail and compared with recent studies. All-normal and anomalous dispersions with small values, very high nonlinear coefficients, and very low confinement losses have been achieved in comparison with the previous publications. The characteristic quantities of the proposed optimal fibers were obtained at the pump wavelength of 2.35 µm including flat dispersion and as small as 1.069 ps/nm.km, non-linear coefficients as high as 62023.377 W−1.km−1, and confinement losses as low as 10−21 dB/m, making them suitable for use in a broadband supercontinuum generation process with a low input power. These fibers are suitable low-cost all-fiber laser sources that effectively replace the current glass fibers.

