Using nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as a catalyst support for selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde
- University of Science and Technology - The University of Danang (DUT)
Abstract
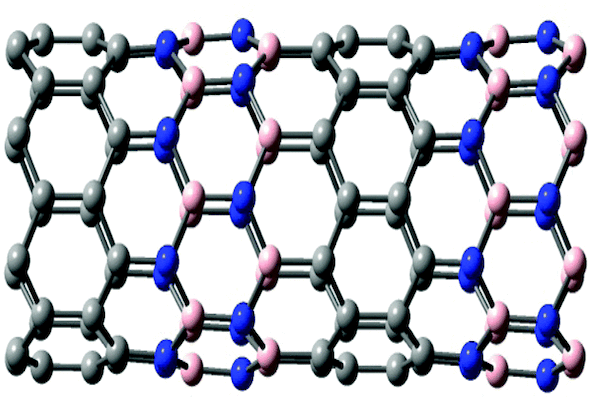
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes (N-CNTs) has been applied in different areas for over two last decade thanks to their novel properties. In this work, N-CNTs were produced by using chemical vapor deposition method, this material was used as catalyst support for nanoparticles paladi (Pd) catalyst. The support and catalyst Pd/N-CNTs were characterized by several techniques including Raman spectrum, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), nitrogen adsorption - desorption isotherms (BET), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The catalyst was tested for the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde (CAL), The result of this study shows that the catalyst Pd/N-CNTs exhibits a high selectivity towards the C=C bond, over 91% of hydrocinnamaldehyde (HCAL) obtained at about 70% of CAL conversion. The obtained results also show that the present nitrogen atoms in the carbon architecture and functional groups of oxygen in the N-CNTs material have altered the surface properties, as enhancing the dispersion and anchoring active phase on the surface of the support.

