Optimization Planning Method of Renewable distributed Generation in Radial Distribution Systems
- Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
- Faculty of Electricity - Electronics - Telecommunications, Can Tho University of Technology, Can Tho City, Viet Nam
Abstract
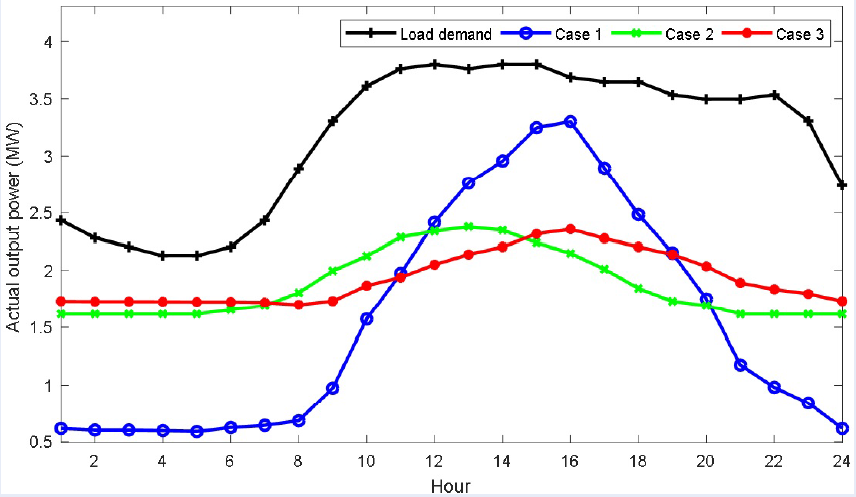
Introduction: This study presents an effective method with high stability called the coyote optimization algorithm (COA) for the optimal integration of renewable distributed generation units (DGUs), including biomass units (BMs), wind turbine units (WTs) and photovoltaic units (PVs). The main aim of the study is to minimize the annual power loss cost considering three hybrid systems with the combination of PV and WT, BM and PV, and BM and WT in the time-varying load demand and operating condition of DGUs simultaneously under constraints of bus voltage, branch current and penetration of DGUs.
Methods: Apply coyote optimization algorithm (COA) for determining the optimal integration of hybrid distribution systems to minimize the annual operating costs.
Results: The obtained results in the IEEE 69-bus radial distribution system have demonstrated that determining the proper integration of DGUs can reduce power loss, save annual operating costs, and improve the voltage profile significantly. In addition, the introduced method (COA) and recently published methods such as the slime mould algorithm (SMA) and improved particle swarm optimization algorithm (IPSO) are also implemented and compared together in solving the optimization problem. Compared to a standard IEEE 69-node system, the hybrid systems with the implementation of COA can reduce the annual power loss cost by 83.84%, 91.27% and 92.74%, respectively. On the other hand, COA can reach smaller annual power loss cost than IPSO by 0.96%, 2.17% and 2.1% and SMA by 0.72%, 1.64%, and 1.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: The results indicate that hybrid systems are operating more effectively than base systems without DGUs, and COA is a strong method providing good solutions for reduction of annual power loss cost.

