A study on the optical properties of a novel flower-core photonic crystal fiber infiltrated with CCl4
- University of Education, Hue University
Abstract
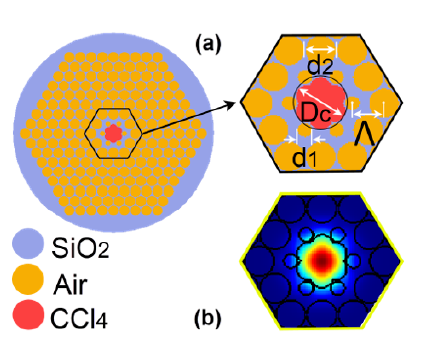
A novel design of photonic crystal fiber with a flower-core is proposed for the first time to optimize dispersion suitable for broadband supercontinuum generation. The numerical simulation of the propagation of light modes in optical fibers is computed by solving Maxwell's wave equations with the full-vector finite-difference eigenmode method. As a result, near-zero ultra-flat all-normal and anomalous dispersion was achieved with fluctuations of ±0.978 ps/nm.km in the 294 nm wavelength region and ±1.168 ps/nm.km in the 432 nm wavelength region, respectively. Furthermore, the dispersion value at the pump wavelength is about 10 times lower than in previous papers. The combination of CCl4 infiltration into the hollow core and the air hole's size heterogeneity in the cladding also enhances the nonlinear properties of the fibers. The effective mode areas less than 2 µm2 at the pump wavelength can help the supercontinuum spectrum to broaden further towards the red wavelength region. Three fibers with structural parameters Ʌ = 0.8 µm, d1/Ʌ = 0.45, Ʌ = 0.9 µm, d1/Ʌ = 0.5, and Ʌ = 0.9 µm, d1/Ʌ = 0.45 are proposed for supercontinuum generation with low peak power due to the nonlinear coefficients as high as hundreds W−1.km−1. These fibers are a new class of optical fibers, highly efficient laser sources that replace traditional glass-core optical fibers.

