Robot Gesture Control using Online Feedback Data with Multi-Tracking Capture System
- Vietnamese-German University, Le Lai st, Hoa Phu ward, Thu Dau Mot city, Binh Duong
- Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vietnamese-German University, Binh Duong, Vietnam
- Mechatronics and Sensor Systems Technology, Vietnamese-German University, Binh Duong, Vietnam
Abstract
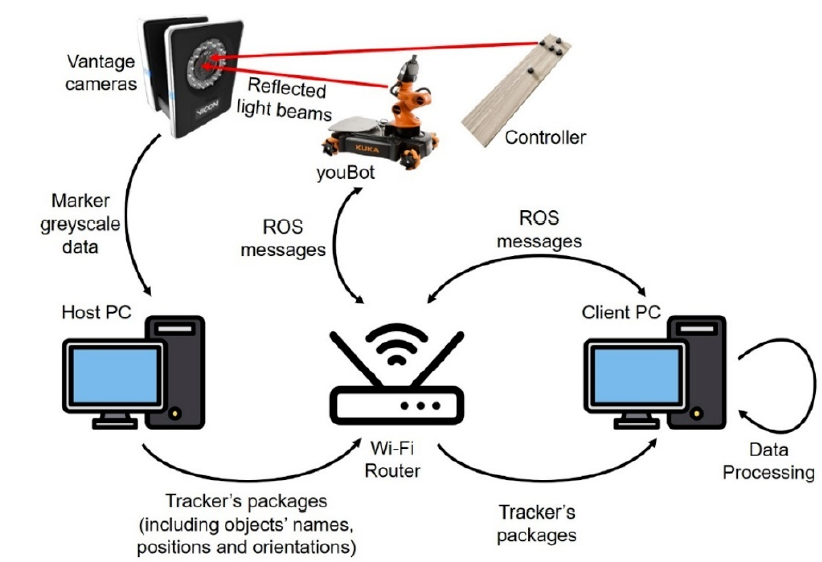
This study employs a Vicon, high-speed and accurate marker-based motion capture system to develop a wireless low-latency gesture control method that requires no additional hardware components or onboard power sources. A novel control method is designed to track a rigid-body object's motion in the workspace and translate it into robot control signals. The system comprises five main components: a host PC with Vicon software named Tracker, a set of eight Vicon Vantage V8 infrared cameras, a client PC that receives Tracker's broadcasted data over Ethernet, a robot model named youBot provided by KUKA, and a rigid-body object that acts as the gesture controller. By using an Application Programming Interface (API) called DataStream, the rigid-body object's pose (position and orientation) can be estimated and used to remotely control the KUKA youBot robot with higher accuracy and an overall reduced latency of 0.3 seconds. In comparison to existing methods based on accelerometer-based and gyroscope-based controllers, the proposed gesture controller uses a set of retro-reflective markers for tracking purposes and requires no additional hardware systems. This proposed control method proves especially beneficial for the robotics prototyping development phase, where different control mechanisms can be easily replicated and tested within the motion capture system's operating range. Additionally, the robot's odometry can also be tracked during testing, making a motion capture system a valuable tool for evaluating motion control methods.

