Controlling the absorption region of multi-shaped silver nanoparticles for SERS applications
- Faculty of Materials Science and Technology, University of Science, 227 Nguyen Van Cu Street, District 5, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
- Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) 700000, Vietnam
- Institute of Applied Materials Science, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST), 29TL Street, Thanh Loc Ward, District 12, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Graduate University of Science and Technology, VAST, Hoang Quoc Viet Street, Cau Giay, Ha Noi, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) are pivotal in advancing surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) due to their exceptional plasmonic properties. Yet, conventional synthesis methods often fail to precisely control their shape and size, impacting SERS efficiency. This study introduces a novel synthesis approach using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to tailor Ag NP morphologies, aiming to optimize their plasmonic resonance for improved SERS detection of hazardous substances.
Methods: We utilized a chemical reduction process with H2O2 to etch and shape Ag NPs, adjusting H2O2 concentrations to control nanoparticle morphology. The characterization of the nanoparticles involved SEM, TEM, and XRD for morphology and structure, with UV-Vis spectroscopy determining their absorption spectra.
Results: The approach yielded Ag NPs with variable shapes and absorption wavelengths (330 nm to 740 nm), directly correlating H2O2 concentration with morphological changes. SEM and TEM showed diverse nanoparticle shapes, and XRD confirmed their crystalline structure. Notably, nanoparticles tuned to specific absorption wavelengths significantly enhanced SERS detection of Rhodamine B.
Conclusion: Our method effectively produces multi-shaped Ag NPs with tunable optical properties, enhancing SERS application in detecting trace organic compounds. This streamlined synthesis process offers new possibilities for environmental monitoring and safety assessments.
INTRODUCTION
Over the decades, nanomaterials have played a crucial role in various scientific fields, contributing significantly to technological advancements and industrial applications1, 2, 3. The synthesis of nanoparticles using various noble metals has attracted considerable research interest due to their unique properties and potential applications in optoelectronics, catalysis, antibacterial agents, bio-sensors, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)4, 5, 6, 7. Among metal nanoparticles, such as Pd, Cu, Au, Zn, Sn, Co, etc., silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) have particularly attracted researchers' attention due to their excellent electrical conductivity and strong plasmonic characteristics8. Numerous studies have shown that the properties of silver nanoparticles depend on their shape, size, size distribution, and crystal structure. For instance, rice-shaped silver nanoparticles exhibit two absorption peaks in the visible and near-infrared regions9, while spherical silver nanoparticles typically show absorption peaks in the near-ultraviolet region10. Additionally, UV-Vis analysis reveals that small silver nanoparticles have high optical absorption and exhibit a redshift11, 12. Consequently, extensive research has been conducted to synthesize silver nanoparticles with controllable morphology and distribution. Various techniques, including chemical methods, microwave techniques, and biological synthesis, have been employed to synthesize silver nanoparticles with diverse shapes, such as spheres, rods, wires, sheets, cubes, and arrays13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20. These methods each have their own advantages for specific synthesis purposes. However, they also face significant limitations, such as low reaction efficiency, time consumption, expensive and complex equipment, and difficulties in size control21. Thus, chemical reduction methods are widely used for synthesizing silver nanoparticles across various fields, including food technology, cosmetics, medical and dental diagnostics, especially in the detection and degradation of harmful organic substances21, 22, 23, 24. For example, a research group led by Jagpreet Singh used Trigonella foenum-graecum (TF) leaf extract as a reducing agent to synthesize silver nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation applications25. In 2017, Mutasem M. Al-Shalalfeh and colleagues used sodium borohydride as a stabilizing and reducing agent to synthesize spherical silver nanoparticles for SERS substrate applications in detecting ketoconazole in agricultural products26. Additionally, Al-Shalalfeh's team fabricated two types of silver nanoparticles using sodium borohydride and trisodium citrate dehydrate, aiming to use them as SERS substrates for detecting 2-thiouracil. The average sizes of these silver nanoparticles were approximately 15 nm and 60 nm, with peak absorption around 400 - 430 nm27. In the VNUHCM Journal of Science and Technology Development, Nguyen Tran Gia Bao developed Ag NPs by reducing silver ions in AgNO3 using sodium borohydride or sodium citrate as reducing agents, along with surface-active agents like poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP), and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The synthesized AgNPs solution, with an absorption peak in the range of 410 - 450 nm, was employed for the detection of organic substances, including Crystal Violet (CV) and Rhodamine B (RhB), at a concentration of 10^-8M28.
In general, the studies mentioned synthesize spherical-shaped silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) with an absorption wavelength of around 400 nm. This characteristic limits their resonance with the excitation wavelengths of lasers commonly used in modern Raman spectroscopy devices (532 nm or 785 nm). Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is significantly augmented by the unique nanostructure of noble metals, which can concentrate light through localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR)8. The surface morphology of nanoparticles leads to varying surface plasmon resonances (SPR)29, making it crucial to develop methods to shift the absorption wavelength to enhance SERS signals. Techniques to modify the absorption of Ag NPs include the electrochemical synthetic method30, irradiation methods31, and chemical reduction32, among others. Yet, chemical synthesis, which involves modifying the shape of pre-formed nanoparticles, remains popular due to its straightforward experimental procedures, high efficiency, and suitability for large-scale production21.
In this study, we synthesized diverse morphologies of silver nanoparticles (MAg NPs) in shapes such as triangular, hexagonal, and disc-shaped, adjusting the peak absorption wavelength between 330 nm and 740 nm by varying the concentration of the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The shape transformation reaction involves reducing silver ions (Ag+) in a spherical silver solution using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in the presence of H2O2 and citrate as a capping agent. Adjusting the H2O2 concentration allows for the development of silver nanoparticles with desired morphology and absorption wavelength to enhance Raman signals. Furthermore, we synthesized a SERS substrate using MAg NPs for detecting Rhodamine B (C28H31ClN2O3), an industrial dye often used in unauthorized food coloring, posing significant health risks. The Raman spectroscopy results demonstrate the substrate's effective detection of Rhodamine B (RhB), suggesting new research avenues in detecting harmful substances in food.
MATERIALS-METHODS
Chemical materials
Silver nitrate (AgNO) - 99% (Sigma-Aldrich), sodium citrate (NaCHO) - 99% (Sigma-Aldrich), sodium borohydrid (NaBH, 98,0%, Scharlau, Spain), hydroxyl peroxide (HO, 30%, Sigma-Aldrich).
Characteristics
Silver nanoparticles' size, morphology, and distribution were analyzed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4800) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL, JEM-1400). The crystal structure of MAg NPs were identified via X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a D8 Advance-Bruker diffractometer operating at 40 kV, 100 mA, with a Cu/Kα radiation source (λ = 0.154 nm). Raman spectra were recorded using a Raman spectrometer with an excitation source at 532 nm.
Fabrication processes
The synthesis process of MAg NPs includes two main steps: nucleation and fabrication of multi-shaped silver nanoparticles.
Three beakers were simultaneously prepared, each containing a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO, 0.25 mM), sodium citrate (NaCHO, 0.25 mM), and sodium borohydride (NaBH, 10 mM), respectively. Subsequently, AgNO and NaCHO were stirred together at room temperature for 30 minutes. Next, NaBH was slowly added to the mixture above, resulting in the formation of a germ solution (Figure 1a).
5ml HO, 0.02M AgNO and 0.05287M NaBH were added to the germ solution which was diluted with DI water (ratio 2:5). The resulting silver solution was then continuously stirred for 30 minutes to stabilize the MAg NPs (Figure 1b).

Synthesis process of a) germ solution and b) multi-shaped silver nanoparticles
RESULTS
The X-ray diffraction pattern of the multi-shaped silver nanoparticles that were synthesized according to the above process is presented in Figure 2b. The diffraction peaks at 2θ values with 27.81°, 32.16°, 38.12°, 46.21°, 54.83°, and 57.39°, correspond to the lattice surfaces (210), (122), (111), (231), (142), and (241) within the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of pure silver (JCPDS, no. 04-0783)33. We synthesized multi-shaped silver solutions labeled as S0, S1, S2, S3, S4, corresponding to different concentrations of HO at 0 %, 7 %, 8 %, 9 %, 10 %, respectively, to investigate the wavelength absorption changes. Also, the absorption spectra of five MAgNPs samples (Figure 2a) revealed peaks at 392 nm, 487 nm, 548 nm, 660 nm, and 738 nm.

a) UV-Vis absorption spectra and b) XRD diffraction pattern of MAg NPs
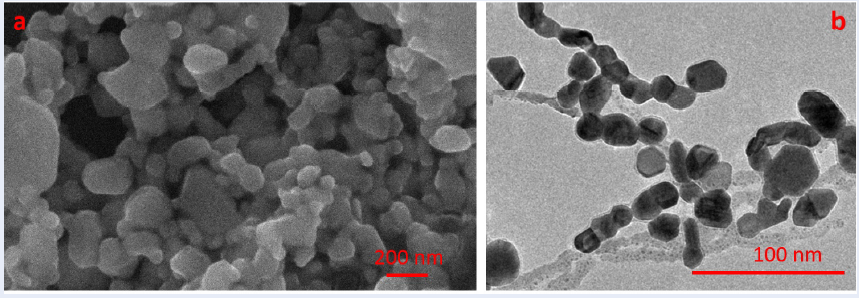
The SEM and TEM images in Figure 3 depict the size and morphology outcomes of MAg NPs. The silver nanoparticle solution prepared exhibits various shapes, including triangles, hexagons, spheres, etc., ranging in size from 30 nm to 150 nm, with an average particle size of 38.641 nm.

a) SEM images and b) TEM images of MAg NPs
The samples with distinct absorption peaks (487 nm, 548 nm, 660 nm, 738 nm) were employed as SERS substrates to explore their efficacy in detecting RhB at a concentration of 1 ppm (Figure 4a). The results reveal that all samples exhibit the capability to amplify Raman signals of RhB at 620, 1197, 1279, 1360, 1509, 1525, 1595, and 1645 cm (
An essential criterion for assessing the reliability of a SERS sample is the synchronization of Raman signals. As depicted in Figure 4b, the SERS signal was examined at random locations on sample S2 with a RhB concentration of 1 ppm.
Band assignment of Rhodamine B
|
Solid Raman |
SERS |
Vibrational Description |
|
619 cm-1 1195 cm-1 1275 cm-1 1356 cm-1 1506 cm-1 1525 cm-1 1595 cm-1 1645 cm-1 |
620 cm-1 1197 cm-1 1279 cm-1 1360 cm-1 1509 cm-1 1525 cm-1 1595 cm-1 1645 cm-1 |
Aromatic bending Aromatic C-H bending C-C bridge-bands stretching Aromatic C-C stretching Aromatic C-C stretching Aromatic C-C stretching C=C stretching Aromatic C=C stretching |

The Raman spectra of RhB (1 ppm) a) based on distinct SERS substrates, and b) at different locations on sample S2
DISCUSSION
In Figure 2b, the diffraction peaks corresponding to the crystallographic planes (210), (122), (111), (231), (142), and (241) of the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of pure silver confirm the formation of silver crystals in the solution after the reaction. Furthermore, the UV-vis absorption spectra reveal the multimodal plasmon resonance oscillations of the MAg NPs. A distinct peak at 338 nm is attributed to the out-of-plane quadrupole plasmon resonance (OPQPR), while absorption bands at 487 nm, 548 nm, 660 nm, and 738 nm in the four MAg NP samples correspond to the in-plane dipole plasmon resonance (IPDPR)36. Additionally, an increase in H2O2 concentration leads to a redshift, suggesting oxidative corrosion of the initial silver seeds and a subsequent increase in size or edge length10. This observation underscores that silver nanoparticles, with their diverse morphologies, often exhibit more complex plasmon vibration modes than simple spheres, enabling control over the absorption wavelength by adjusting the H2O2 concentration. The size and morphological characteristics of the MAg NPs, as shown in Figure 3, also demonstrate the successful synthesis of multi-shaped silver nanostructures through the growth corrosion method. The investigation of the Rhodamine B (RhB) detection capability of the SERS substrate based on MAg NPs, presented in Figure 4a, clearly indicates that all samples enhance Raman signals through characteristic oscillations as detailed in
The etching-growth process, which employs hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), was used to produce multi-shaped silver nanoparticles with the desired absorption wavelength. The synthesis procedure consists of two main stages: the corrosion stage and the growth stage. Importantly, the corrosion process is crucial in determining the final structure of the nanocrystals. It accomplishes this by either completely removing energetically unfavorable particles or by etching to form sharp corners and edges37. Hydrogen peroxide exhibits aspect-selective corrosive properties towards metallic silver species while also acting as a reducing agent for silver ionic species, as demonstrated by equations (1) to (5)38, 39, 40, 41.
Ag + e → Ag (E = 0.7996 V) (1)
HO + 2e → 2HO (E = 0.867 V) (2)
2Ag + HO → Ag + 2HO (E = 0.068 V) (3)
HO + 2HO → 2HO + O + 2e (E = 0.146 V) (4)
HO + 2Ag + 2HO → 2Ag + 2HO + O (E = 0.947 V) (5)
During the growth period, AgNO and NaBH are introduced sequentially, resulting in the reduction of Ag ions and the generation of MAg NPs, as illustrated by the following equation (6):
2Ag + 4BH + 7HO → 2Ag + BO + 15H (6)
Due to its potent reducing capability, NaBH rapidly reduces Ag ions and facilitates the growth of symmetrical facets in MAg NPs and secondary seed particles . Consequently, the resulting silver nano solution exhibits diverse morphologies, resulting in varying absorption wavelengths when altering the HO concentration.
CONCLUSIONS
Multi-shaped silver nanoparticles were successfully synthesized, exhibiting absorption at distinct wavelengths (487, 548, 660, and 738 nm) through a rapid and straightforward process. Notably, among these nanoparticles, those with an absorption peak at 548 nm demonstrated superior enhancement of the Raman signal for Rhodamine B (RhB) at a concentration of 1 ppm. Furthermore, the corrosion-growth mechanism behind the formation of these nanoparticles has been elucidated. We anticipate that the findings from this study will pave the way for the application of silver nanoparticles in various fields, especially in detecting low-concentration toxic organic compounds in the future.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors assert that there are no conflicts of interest related to the publication of this article.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTIONS
L. N. T. Nguyen: carried out the experiment, writing manuscript. L. T. Duy, N. B. T. Pham: measured and analyzed UV-Vis, XRD data. L. N. T. Nguyen, C. K. Tran: measured, analyzed SEM, TEM data. N. P. Nguyen, H. N. Luong: investigated SERS effect through measuring and analyzing Raman Spectra. V. Q. Dang: managed the experiment, collected data to write the paper.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research is funded by Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under grant number B2023-18-14.

