Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Phlogacanthus turgidus Leaf Extract: Catalytic Activity in TMB-H2O2 Redox Reactions and their Application in Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing
Abstract
Introduction: Among metal nanoparticles (MNPs), silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have partical attention due to their excellent electrical and optical properties. Notably, colorimetric sensors incorporating metal nanoparticles have garnered significant attention from scientists in biochemical analysis, offering a simple solution. Here, we report the use of AgNPs applying hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sensor. Methods: The AgNPs were synthesized using Phlogacanthus turgidus leaf extract, H2O2 oxidized colorless TMB into blue ox-TMB, the reaction was catalyzed by AgNO3. Measuring the resulting solution spectrophotometrically helped to determine the concentration of ox-TMB, thereby determining the concentration of H2O2 produced. Results: The UV-Vis spectrum of AgNPs synthesized from Phlogacanthus turgidus leaf extract exhibited a prominent absorption peak at 427 nm. The linear range was determined in 100 – 300 µM. The linear regression equation is y = 0.91574 + 3.10484×10-4 CH2O2 with a SD value of 0.00438. The result showed that the limit of detection (LOD) of H2O2 through the color reaction between the 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and H2O2 in AgNPs catalysis was 46.55 µM and the limit of quantification (LOQ) was 141.07 µM. Conclusion: Based on the results of optimal conditions for TMB oxidation in the presence of AgNPs, we can evaluate the applicability as a H2O2 sensor.
Introduction
MNPs have recently become a topic of interest because of their diverse applications1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. MNPs are important materials used in the fields of biomedicine, optics, the environment, catalysis and electrochemistry, such as biosensors 7, 8, 9, 10, 11. Among MNPs, AgNPs have received particular attention because of their excellent electrical and optical properties 12. HO is a powerful oxidizing agent with various applications in medicine and industry. It is commonly known as a bleaching and disinfecting agent. However, proper handling is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness, as it is highly corrosive and can alter stem cells and pose acute and chronic toxicity risks to aquatic environments13, 14, 15. HO is measured and quantified across a wide range of sample matrices, including environmental samples (water and soil), human fluids (sweat and blood), and cell and tissue cultures. Various methods are employed for this purpose, including optical techniques (colorimetry, chemiluminescence, and fluorescence), as well as electrochemical methods (potentiometry, voltammetry, and amperometry). Notably, colorimetric sensors incorporating metal nanoparticles have garnered significant attention from scientists in biochemical analysis, offering a simple solution16.
Recently, many studies have investigated the green synthesis and application of AgNPs in HO sensors. Nurul Ismillayli et al. (2024) reported the use of microwave-assisted synthesis of AgNPs as a colorimetric sensor for HO17. Ramesh Vinayagam et al. (2024) studied the structural characterization of marine macroalgae-derived AgNPs and their colorimetric sensing of HO18. Haodong Shen et al. (2023) reported a one-step synthesis of nanosilver embedding laser-induced graphene for HO sensors 19. However, there has been no research on the synthesis of AgNPs from leaf extract for application as HO detectors on the basis of the reduction reactions of TMB and HO in AgNP catalysis. The reduction in TMB is illustrated in Figure 1. In this strategy, the AgNPs act as catalysts, and the oxidation product of TMB possesses a blue color, which can be determined via UV‒Vis spectroscopy. The catalytic mechanism of AgNPs involves three primary steps: (1) the generation of hydroxyl radicals (OH), (2) the production of oxygen (O), and (3) electron transfer, as illustrated in Figure 120. Moreover, the extract of the leaf contains high levels of polyphenols21, which have the ability to reduce and stabilize metallic nanoparticles. In this study, leaf extract was used to synthesize AgNPs, and the catalytic ability of AgNPs in the redox reaction between HO and TMB was investigated.

Oxidation mechanism of TMB using H2O2 in the presence of a AgNP catalyst.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
leaves were collected from Bu Gia Map National Park, Binh Phuoc Province, Vietnam. Chemicals including silver nitrate (AgNO), 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (CHN), hydrogen peroxide (HO), acetic acid (CHCOOH) and sodium acetate (CHCOONa), which were of analytical grade without further purification, were purchased from Acros Co., Belgium. Deionized water was thoroughly utilized in all the experiments.
Methods
Synthesis of AgNPs from leaf extract
The synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) was performed via leaf extract, following previous reports2, 5. Specifically, 0.25 mL of leaf extract was mixed with 5 mL of an aqueous AgNO₃ solution under reaction conditions of 2.0 mM silver ion concentration, 80°C, and a reaction time of 70 minutes. The formation of AgNPs was verified via UV–Vis spectrophotometry. The synthesized AgNP solution was subsequently stored at 8°C for future applications.
Determination of the optimal temperature for the TMB and HO reactions with the AgNP catalyst
To optimize the reaction temperature, 400 µL of 5 mM TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution (pH 5), 600 µL of 400 µM H₂O₂, and 150 µL of the synthesized AgNP solution were each carefully added to a 10 mL bottle. The bottle was covered with foil to protect it from light and placed in a thermostatic bath at various temperatures (30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, 55°C, and 60°C) for 30 minutes. Following incubation, UV‒Vis spectroscopy was used to measure the absorbance of the solutions to determine the optimal temperature for the reaction of TMB and H₂O₂ in the presence of the AgNP catalyst.
Determination of the optimal time for the TMB and H₂O₂ reactions with the AgNP catalyst
To determine the optimal reaction time, 400 µL of 5 mM TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution (pH 5), 600 µL of 400 µM H₂O₂, and 150 µL of the AgNP solution were added to a 10 mL container, which was carefully covered with foil. This container was then placed in a thermostatic reaction tank set to the optimal temperature. UV‒Vis spectroscopy measurements were taken at 10-minute intervals to identify the optimal reaction time for the interaction between TMB and H₂O₂ in the presence of the AgNP catalyst.
Determination of the optimal pH for the TMB and H₂O₂ reactions with the AgNP catalyst
To optimize the pH for the reaction, 400 µL of 5 mM TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution at various pH values, 600 µL of 400 µM H₂O₂, and 150 µL of the AgNP solution were added to 10 mL bottles and covered with foil. These bottles were then placed in a thermostatic bath set to the optimal temperature and time. UV‒Vis spectroscopy measurements were conducted to identify the optimal pH for the TMB and H₂O₂ reactions in the presence of the AgNP catalyst.
Determination of the optimal AgNP concentration for the TMB and HO reactions with the AgNP catalyst
To optimize the concentration of AgNPs, 400 µL of 5 mM TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution (adjusted to the optimal pH), 600 µL of 400 µM H₂O₂, and varying volumes of the AgNP solution (60 µL, 70 µL, 80 µL, 90 µL, 100 µL, 110 µL, 120 µL, and 130 µL) were added to separate 10 mL bottles, each covered with foil. These bottles were then placed in a thermostatic bath set to the optimal temperature and time. UV‒Vis spectroscopy was used to determine the optimal concentration of AgNPs for the TMB and H₂O₂ reactions.
Determination of the optimal TMB concentration for TMB and HO reactions with AgNP catalysts
To determine the optimal concentration of TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution (adjusted to the optimal pH), 600 µL of 400 µM H₂O₂, the optimal volume of AgNP solution (determined ), and varying concentrations of TMB (400 µL of 3 mM, 3.5 mM, 4 mM, 4.5 mM, 5 mM, 5.5 mM, 6 mM, or 6.5 mM) were added to separate 10 mL bottles, which were covered with foil. These bottles were then placed in a thermostatic bath set to the optimal temperature and time. UV‒Vis spectroscopy was performed to determine the optimal TMB concentration for the TMB and H₂O₂ reactions catalyzed by the AgNPs.
Determination of the linear range and limit of detection (LOD) value
To determine the optimal concentration of H₂O₂, 400 µL of TMB, 2 mL of acetate buffer solution (adjusted to the optimal pH), and the optimal volume of AgNP solution were combined with varying concentrations of H₂O₂ (600 µL of 10 µM, 50 µM, 100 µM, 150 µM, 200 µM, 250 µM, 300 µM, 350 µM, and 400 µM) in separate 10 mL bottles, each covered with foil. These bottles were placed in a thermostatic bath set to the optimal temperature and time. UV‒Vis spectroscopy was conducted on the solutions to identify the optimal concentration of H₂O₂ for the reaction with TMB catalyzed by AgNPs. The limits of detection (LODs) and limits of values were calculated via Equations (1) and (2), respectively:
where SD and a are the standard deviation and slope of the linear regression line, respectively.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Synthesis of AgNPs from leaf extract
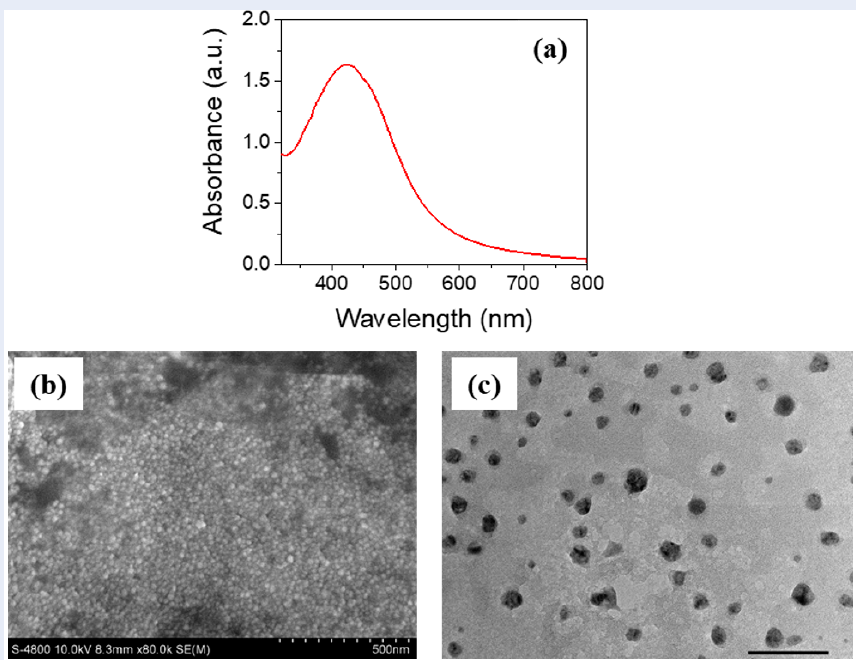
Figure 2a shows that the peak absorption of the AgNPs synthesized from leaf extract was in the wavelength range of 400–500 nm. The UV‒Vis spectrum of the AgNPs synthesized from leaf extract exhibited a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at 427 nm. Microscopy images (Figure 2b and Figure 2c) revealed that the structure of the AgNPs consisted mostly of spheres with an average size of 13 nm, which aligns with the findings of a previous study 2.

UV–Vis spectra (a) and SEM (b) and TEM (c) images of AgNPs synthesized from
Optimization of the TMB and HO reactions with the AgNP catalyst
Figure 3 shows the UV‒Vis spectra of TMB oxidation as a function of reaction temperature. The absorption spectra were recorded over a temperature range from 20°C to 60°C. The data indicated that the absorbance at a wavelength of 654 nm increased progressively with temperature, reaching a maximum at 35°C. Beyond this temperature, a decrease in absorbance was observed, which was likely attributed to the thermal instability of ox-TMB at higher temperatures. Accordingly, 35°C was identified as the most favorable temperature for the efficient oxidation of TMB by H₂O₂, facilitated by the AgNP catalyst.

Absorption spectra from the temperature investigation with the AgNP catalyst (a) and the dependence of the absorbance on the reaction temperature (with the AgNP catalyst) (b).
Results of the optimal time for the reaction of TMB and H₂O₂ with the AgNP catalyst
The effect of reaction time on TMB oxidation was evaluated at the optimal temperature of 35°C, with measurements taken at 10-minute intervals to identify the optimal reaction duration. The absorbance data obtained via UV‒Vis spectroscopy are presented in Figure 4. Superimposing the absorption spectra for various time points revealed that the reaction conducted for 30 minutes presented the highest absorbance intensity at 654 nm. This observation suggests that extended reaction times under these conditions may lead to the degradation of -TMB. Therefore, a reaction time of 30 min was determined to be the most suitable condition for the oxidation of TMB by H₂O₂ in the presence of the AgNP catalyst, starting from the moment the sample was introduced into the thermostatic bath.

Absorption spectra over time (a) and dependence of the absorbance on the reaction time with the AgNP catalyst (b).
Results of the optimal pH for the reaction of TMB and H₂O₂ with the AgNP catalyst
pH plays a principal role in regulating the oxidation rate of TMB. UV‒Vis spectra were recorded and compared for samples prepared under various pH conditions, as illustrated in Figure 5. The data revealed that samples with a pH of 4 presented the highest absorbance intensity at 654 nm, while this intensity progressively decreased for samples with low or high pH values. This trend can be attributed to the reaction equilibrium under highly acidic conditions (pH < 4.0) shifting toward the formation of -TMB. Conversely, at higher pH values, the decreasing formation efficiency of the colored product at 654 nm may result from the elevated redox potential of the substrates, leading to decreased susceptibility to oxidation22. Consequently, pH 4 was identified as the optimal condition and was selected for further exploration of the factors influencing the TMB redox process with H₂O₂ in the presence of an AgNP catalyst.

Absorption spectrum of the pH survey (a) and dependence of the absorbance on the pH value of the AgNP catalyst (b).
The effects of the optimal AgNP concentration on the TMB and HO reactions
A survey was conducted to investigate the influence of the AgNP catalyst volume on the absorption intensity of the samples in solution. The absorption spectra of the solutions containing TMB, acetate buffer (pH 4), H₂O₂, and various volumes of the AgNP catalyst were analyzed (Figure 6). At a wavelength of 654 nm, the absorption intensity increased progressively as the AgNP volume increased from 60 µL to 120 µL under constant conditions of TMB concentration, acetate buffer, and H₂O₂. However, a significant decrease in the absorption intensity was observed in the sample containing 130 µL of the AgNP catalyst. This indicated that increasing the catalyst volume increased the surface area, thereby improving the catalytic efficiency of the oxidation‒reduction reaction. Nevertheless, an excessive amount of AgNPs likely resulted in the decomposition of H₂O₂, reducing the reaction yield. Therefore, 120 µL of AgNP catalyst was identified as the optimal volume and was selected for subsequent investigations of other reaction parameters.

Absorption spectrum of the AgNP catalyst quantity survey (a), and the absorption depends on the amount of AgNP catalyst (b).
The effects of the optimal TMB concentration on the TMB and HO reactions with the AgNP catalyst
The TMB concentration is a critical parameter for evaluating the reaction efficiency between TMB and HO in the presence of the synthesized AgNP catalyst. Figure 7 shows the dependence of the reaction efficiency on the TMB concentration through changes in the absorption intensity observed in the UV‒Vis spectra at 654 nm. The results revealed that the absorption intensity increased with increasing TMB concentration, reaching a maximum at 5.5 mM. Above this concentration, the absorbance decreased significantly, likely due to the oxidation of monoamine groups in TMB at higher concentrations. Consequently, a TMB concentration of 5.5 mM was selected as the optimal condition for the redox reaction between TMB and HO in the presence of the AgNP catalyst.

Absorption spectrum of the TMB concentration survey (a) and dependence of the absorbance on the TMB concentration with the AgNP catalyst (b).
Influence of the HO concentration on the TMB and HO reactions with the AgNP catalyst
Figure 8 shows the dependence of the absorbance values on the HO concentration. The absorbance intensity at 654 nm increased with increasing HO concentration, reaching a maximum at 350 µM. Beyond this concentration, the TMB concentration appeared insufficient to react fully with HO. A linear relationship was observed within the range of 100–300 µM, described by the regression equation y = 0.91574 + 3.10484×10 C, with a standard deviation (SD) of 0.00438. The limit of detection (LOD) for HO, which is based on the colorimetric reaction between oxidized TMB (ox-TMB) and HO catalyzed by AgNPs, was determined to be 46.55 µM, with a limit of quantification (LOQ) of 141.07 µM. These findings, combined with the optimal conditions for TMB oxidation shown in Table 1, underscore the potential of AgNPs as effective catalysts in the TMB-HO redox reaction, demonstrating their applicability as sensitive HO sensors.

Absorbance dependence on the H2O2 concentration.
Optimal conditions for TMB oxidation in the presence of AgNPs.
|
Parameters |
Optimal values |
|
Temperature (oC) |
35 |
|
Time (minute) |
30 |
|
pH |
4.0 |
|
AgNPs catalyst (µL) |
120 |
|
TMB (mM) |
5.5 |
|
Concentration range linear H2O2 (µM) |
100 - 300 |
CONCLUSIONS
AgNPs were synthesized from leaf extract, resulting in absorption peaks in the wavelength range of 400–500 nm. This investigation of the conditions affecting the oxidation of TMB with HO with the AgNP catalyst provides the best conditions for the detection of HO through the TMB reaction with the AgNP catalyst. The optimal conditions (temperature, time, pH, AgNP concentration, TMB concentration, and HO concentration) for TMB oxidation in the presence of HO were 35°C, 30 min, pH 4, 120 µL of AgNPs, 5.5 mM TMB, and HO concentrations ranging from 100–300 µM. Therefore, we can evaluate the applicability of HO in wastewater.
Abbreviations
None.
Acknowledgments
None.
Author’s contributions
All authors equally contributed to this work, read and approved the final version of the manscript for publishing.
Funding
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 104.99--2021.56
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

