Phenolic compounds from the bark of Aglaia lawii and their cytotoxic activity against HepG2
- Faculty of Chemistry, VNUHCM-University of Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: Aglaia lawii is a large tree belonging to the Meliaceae family. In traditional medicine, the stem bark is used as a vermicide while the leaves are used for the treatment of headache. Studies on the chemical constituents of this species in Vietnam and its biological activity, especially its ability to treat liver cancer, are still limited. This work describes the isolation and structure elucidation of six phenolic compounds from an ethyl acetate extract of the bark of A. lawii as well as the evaluation of cytotoxic activity against HepG2.
Methods: The extracts were prepared by extracting the dried ground bark using Soxhlet extraction. Isolation was performed using column chromatography over silica gel, RP-18 and using gel permeation chromatography over Sephadex LH-20. Chemical structures were elucidated using spectroscopic methods (1D- and 2D-NMR, HR-ESI-MS and IR) and comparison of spectral data with those in literature. Cytotoxic activity against HepG2 human liver cancer cells was evaluated in vitro using the MTT assay.
Results: Six phenolic compounds, palmarumycin JC2 (1), 5-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone (2), coniferaldehyde (3), 3-hydoxy-1-(4¢-hydroxy-3¢-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one (4), p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (5), and vanillin (6), were isolated from an ethyl acetate extract of the bark of A. lawii collected in Dong Nai Province. Compounds 1-3 were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells and the result showed that the compounds exhibited weak effects or no activity.
Conclusion: All the isolated compounds have been reported from this species for the first time. It is also the first report on the cytotoxicity of 1-2 against HepG2 cells although the compounds displayed weak effects.
Keywords: Aglaia lawii; phenolic compounds, cytotoxicity, HepG2
INTRODUCTION
is the largest genus of the Meliaceae family and consists of approximately 250 species1. (Wight) Fald. ex Raman2 or (Wight) C.J. Saldanha (synonyms: , )3 is found mainly in India, Bhutan, China, and Southeast Asia, including Vietnam, Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Laos1. In folk medicine, the leaves are used for the treatment of headache2, and the stem bark is used as a vermicide4. Previous phytochemical investigations of this species have revealed the significant existence of limonoids4, 5, 6, triterpenoids7, 8, sesquiterpenoids5, 9, and steroids10, which exhibit diverse pharmacological activities, such as cytotoxic7, anti-inflammatory9, 10, 11, antiallergic11, and anti-HIV-112 properties. In this work, we report the isolation and structural characterization of six phenolic compounds (1--6) from the ethyl acetate of the bark of . Furthermore, the in vitro cytotoxic activity of the isolated compounds against HepG2 human liver cancer cells was evaluated via the MTT assay to identify active compounds with therapeutic effects on liver cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General experimental procedures
Optical rotation was measured via a P8000 polarimeter manufactured by A. Krüss Optronic, whereas HR-ESI-MS data were recorded via an Agilent 6500 series Q-TOF mass spectrometer. IR spectra were recorded with KBr using a JASCO FT/IR-6600 spectrometer. NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker AV 500 (500 MHz for H and 125 MHz for C) with CDCl, acetone- or methanol- as the solvent and calibrated on the basis of the chemical shifts of the corresponding deuterated solvents13. Column chromatography (CC) was run on silica gel (Merck, 40–63 mm)- or RP-18 (Merck, 40–63 mm)-bonded phases. For gel permeation chromatography (GPC), Sephadex LH-20 (GE Healthcare) was used. TLC was carried out on TLC silica gel (Merck, 250 mm)- or RP-18 (Merck, 200 mm)-precoated aluminum plates. The TLC plates were visualized via UV light, sprayed with ethanolic ferric chloride or vanillin-HSO in EtOH, and then heated at approximately 120 °C for several minutes.
Fetal bovine serum (FBS), minimal essential medium with Eagle salt (MEME), and ellipticine were purchased from Sigma. HepG2 cells (HB-8065) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. Cytotoxic activity was determined in Costar 96-well plates.
Plant material
The bark of was collected at the Center for Experimental Forest Research in Eastern South Vietnam (formerly known as Trang Bom Plant Collection Garden), Dong Nai Province, in November 2019. According to the document kept at the Center, the plant has been cultivated at Lot H with Code Number 83, Vietnamese name: Gội bốn cánh.
Extraction and isolation
The dried, ground bark (10 kg) was extracted with EtOAc and MeOH, respectively, via a Soxhlet extractor. Removing the solvents via a rotary evaporator produced an EtOAc extract (110 g) and a MeOH extract (138 g). The CC of the EtOAc extract with silica gel (-hexane-EtOAc 0--100%) furnished 10 fractions (F1--10). Fraction F6 (9.5 g) was separated via CC on silica gel (-hexane-EtOAc 0-50%) to afford 8 fractions (F6.1--8). Further separation of fraction F6.2 (1.22 g) via CC on silica gel (-hexane-CHCl 30--100%) afforded eight fractions (F6.2.1--8). Fraction F6.2.5 (30.5 mg) was purified via CC on RP-18 (70–100% MeOH in HO) to give 2 (5.4 mg). Fraction F6.3 (835 mg) was separated via repeated CC on silica gel (-hexane-EtOAc 0–70%) to obtain 1 (24.5 mg). F6.4 (600 mg) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 (CHCl-MeOH 1:1) and then purified via CC on silica gel (-hexane-EtOAc 0--40%) to produce 3 (12.6 mg) and 4 (3.5 mg). F6.6 (1.64 g) was subjected to CC on silica gel (-hexane-acetone 0--40%) to furnish five fractions (F6.6.1--5). The purification of fraction F6.6.2 (83.0 mg) via Sephadex LH-20 (CHCl-MeOH 1:1) yielded 5 (7.2 mg). The CC of fraction F6.6.4 (55.0 mg) on silica gel (-hexane-EtOAc, 0–40%) led to the isolation of 6 (4.4 mg).
Cytotoxicity assay
The MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium) assay was carried out via the method described by Mosmann14, with ellipticine used as the positive control (n = 3). The cells were cultured in MEME supplemented with 10% FBS at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO. Ellipticine was dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 0.01 mM. Briefly, HepG2 cells were separated with trypsin, seeded in each well at 3 × 10 cells/mL, treated with the test compounds at concentrations of 256, 64, 16, 4 and 1 µg/ml for 72 hours under standard conditions, and then stained with 10 µl of MTT (5 mg/ml) for 4 hours. The formazan crystals were dissolved in 100 µl of DMSO after the environmental solutions were removed. Optical density (OD) values were measured at a wavelength of 540 nm via a 96-well microtiter plate reader (Synergy HT, Biotek Instruments). The percentage of growth inhibition (I%) was calculated according to the formula:
: Optical density values of the tested sample
: Optical density values of the control sample.
The IC values were calculated via nonlinear regression via RawData software (Gen5 2.07.17).
RESULTS
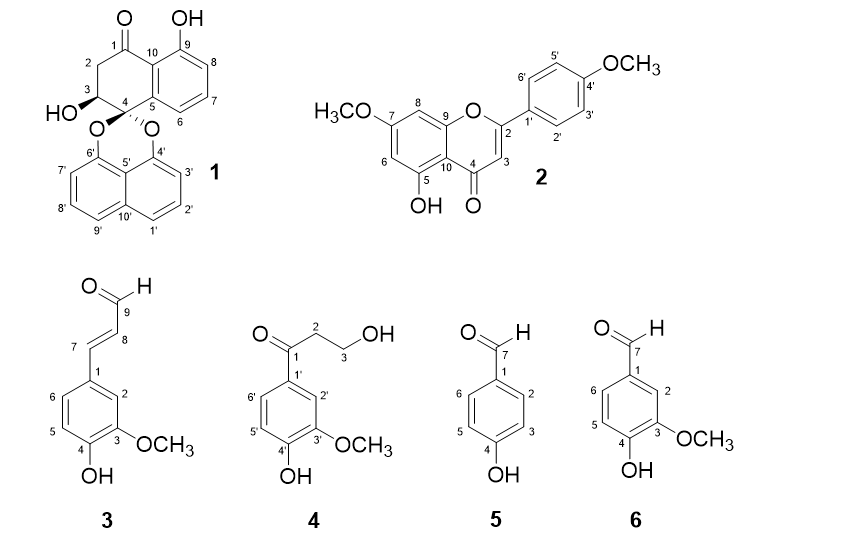
From the ethyl acetate extract of the bark of , six compounds (1--6) were isolated via chromatographic methods. Their structures are shown in Figure 1.
Palmarumycin JC2 (1): yellow needles. +142.4 ( 7 mg in 1 ml CHCl); IR (KBr) : 3452, 3059, 2924, 1643, 1612, 1554, 1269, 814, 756 cm. HR-ESI-MS: 333.0758 [M–H] (calculated for CHO 333.0768). H-NMR (CDCl, 500 MHz): 13.84 (1H, s, 9-OH), 7.55 (3H, m, H-7, H-1', H-9'), 7.49 (1H, t, 8.0 Hz, H-2'), 7.44 (1H, t, 7.9 Hz, H-8'), 7.33 (1H, dd, 7.6, 1.0 Hz, H-6), 7.08 (1H, d, 8.3 Hz, H-8), 7.08 (1H, d, 8.3 Hz, H-3'), 6.92 (1H, d, 7.5 Hz, H-7'), 4.60 (1H, t, 3.7 Hz, H-3), 3.24 (1H, dd, 17.8, 3.4 Hz, H-2a), 2.95 (1H, dd, 17.8, 4.0 Hz, H-2b); C-NMR (CDCl, 125 MHz): δ 201.1 (C-1), 162.3 (C-9), 147.3 (C-6'), 146.5 (C-4'), 138.1 (C-5), 134.3 (C-10'), 137.2 (C-7), 127.9 (C-2'), 127.8 (C-8'), 121.3 (C-9'), 121.6 (C-1'), 120.0 (C-8), 118.1 (C-6), 115.5 (C-10), 113.3 (C-5'), 109.7 (C-3'), 109.0 (C-7'), 98.9 (C-4), 67.4 (C-3), 41.4 (C-2) (H- and C-NMR assignments were performed using HSQC, HMBC and COSY techniques).
5-Hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone (2): yellow needles. H-NMR (CDCl, 500 MHz): 12.80 (1H, s, 5-OH), 7.84 (2H, d, 8.9 Hz, H-2'/H-6'), 7.01 (2H, d, 8.9 Hz, H-3'/H-5'), 6.57 (1H, s, H-3), 6.48 (1H, d, 2.2 Hz, H-8), 6.36 (1H, d, 2.2 Hz, H-6), 3.89 (3H, s, 7-OCH), 3.88 (3H, s, 4'-OCH); C-NMR (CDCl, 125 MHz): δ 182.6 (C-4), 165.6 (C-7), 164.2 (C-2), 162.8 (C-4'), 162.4 (C-5), 157.9 (C-9), 123.8 (C-1'), 128.2 (C-2'/C-6'), 114.7 (C-3'/C-5'), 105.8 (C-10), 104.5 (C-3), 98.2 (C-6), 92.8 (C-8), 55.9 (4'-OCH), 55.7 (7-OCH).
Coniferaldehyde (3): yellowish needles. H-NMR (CDCl, 500 MHz): 9.65 (1H, d, 7.7 Hz, H-9), 7.40 (1H, d, 15.8 Hz, H-7), 7.12 (1H, dd, 8.2, 1.9 Hz, H-6), 7.07 (1H, d, 1.9 Hz, H-2), 6.96 (1H, d, 8.2 Hz, H-5), 6.60 (1H, dd, 15.8, 7.7 Hz, H-8), 3.95 (3H, s, 3-OCH); C-NMR (CDCl, 125 MHz): δ 193.9 (C-9), 153.4 (C-7), 149.3 (C-3), 147.4 (C-4), 127.1 (C-1), 126.9 (C-8), 124.5 (C-6), 115.3 (C-5), 109.9 (C-2), 56.4 (3-OCH).
3-Hydoxy-1-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one (4): White crystals. H-NMR (CDCl, 500 MHz): 7.55 (2H, m, H-2', H-6'), 6.96 (1H, d, 8.0 Hz, H-5'), 4.02 (1H, t, 5.3 Hz, H-3), 3.96 (3H, s, 3'-OCH), 3.18 (1H, t, 5.3 Hz, H-2); C-NMR (CDCl, 125 MHz): δ 199.2 (C-1), 151.0 (C-4'), 146.9 (C-3'), 129.9 (C-1'), 123.8 (C-6'), 114.1 (C-5'), 109.8 (C-2'), 58.5 (C-3), 56.3 (3'-OCH), 40.0 (C-2).
-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (5): white crystals. H-NMR (acetone-, 500 MHz): 9.85 (1H, s, H-7), 7.80 (2H, d, 8.5 Hz, H-2, H-6), 7.00 (2H, d, 8.5 Hz, H-3, H-5);C-NMR (acetone-d, 125 MHz): δ 191.0 (C-7), 164.0 (C-4), 132.8 (C-2, C-6), 130.5 (C-1), 116.7 (C-3, C-5).
Vanillin (6): white needles. H-NMR (methanol-, 500 MHz): 9.74 (1H, s, H-7), 7.44-7.41 (2H, m, H-2, H-6), 6.93 (1H, d, 6.6 Hz, H-5), 3.91 (3H, s, 3-OCH); C-NMR (methanol-, 125 MHz): δ 191.5 (C-7), 153.4 (C-3), 148.3 (C-4), 129.3 (C-6), 126.5 (C-1), 114.9 (C-5), 109.9 (C-2), 55.0 (3-OCH).

Structures of compounds 1-6
Cytotoxicity of compounds 1--3 against HepG2 cells
Palmarumycin JC2 (1): IC = 36.09 ± 3.79 µg/ml; 5-Hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone (2): IC > 256 μg/ml; Coniferaldehyde (3): IC = 53.20 ± 4.37 µg/ml; Ellipticine (positive control): IC = 0.45 ± 0.04 µg/ml.
DISCUSSION
Compound 1 was obtained as yellow needles, +142.4 ( = 0.7, CHCl). Its molecular formula was determined to be CHO by HR-ESI-MS ([M–H] 333.0758, calculated for CHO 333.0763), indicating that 1 had fourteen degrees of unsaturation. The H-NMR spectrum showed resonances for the presence of a chelated hydroxy proton [ 13.84 (s, 9-OH)], a 1,8-disubstituted naphthalene moiety [ 7.55 (2H, m, H-1', H-9'), 7.49 (1H, t, 8.0 Hz, H-2'), 7.44 (1H, t, 7.9 Hz, H-8'), 7.08 (1H, d, 8.3 Hz, H-3'), 6.92 (1H, d, 7.5 Hz, H-7')], three aromatic protons of a 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzene ring [ 7.55 (1H, m, H-7), 7.33 (1H, dd, 7.6, 1.0 Hz, H-6), 7.08 (1H, d, 8.6 Hz, H-8)], an oxymethine proton of a secondary alcohol [ 4.60 (1H, t, 3.7 Hz, H-3), two protons of a methylene group lying between two electron-withdrawing groups [ 3.24 (1H, dd, 17.8, 3.4 Hz, H-2a), 2.95 (1H, dd, 17.8, 4.0 Hz, H-2b)]. The C-NMR spectrum had signals due to 20 carbons, comprising a 1,8-disubstituted naphthalene moiety carrying two oxygenated carbons [δ 147.3 (C-6'), 146.5 (C-4')], a trisubstituted benzene ring carrying an oxygenated carbon [δ 162.3 (C-9)], a conjugated carbonyl carbon [ 201.1 (C-1)], a spiroketal carbon [ 98.9 (C-4)], an oxymethine carbon [ 67.4 (C-3)], and a methylene group [ 41.4 (C-2)]. The planar structure of 1 was elucidated by analysis of its HSQC, HMBC, and COSY spectra. In the COSY spectrum, correlations between H-2 and H-3 revealed a bond between C-2 and C-3. In the HMBC spectrum, proton H-2 correlated with C-1, C-3, C-4 and C-10, whereas proton H-3 presented cross-peaks at C-1, C-4 and C-5, indicating a 1-tetralone subunit that carried a secondary alcohol at C-2 and a spiroketal carbon at C-4. Other HMBC and COSY correlations revealed the presence of a 1,2,3-trisubstituted benzene ring of the 1-tetralone subunit and a 1,8-dioxygenated naphthalene moiety in the molecule (Figure 2). The spectral data, along with the lack of one degree of unsaturation, indicated that the 1-tetralone fragment was bonded to the 1,8-dioxygenated naphthalene moiety via the spiroketal carbon [ 98.9 (C-4)]. On the basis of the spectral analysis and comparison of the data with the published article,15, 16 compound 1 could be (3)- almarumycin JC2 (+131.9 ( = 0.5, CHCl)15 or the enantiomer (3)- almarumycin BG1 (–151.0 ( = 0.5, CHCl)16. Since the optical rotation of compound 1 was +142.4 ( = 0.7, CHCl), it was identified as almarumycin JC2, which was previously isolated from .15

1H-1H COSY and selected HMBC correlations of 1
Compound 2 was isolated as a yellow needle. The H-NMR spectrum showed resonances for the presence of a chelated hydroxy proton [ 12.80 (1H, , 5-OH)], an isolated olefinic proton [ 6.57 (, H-3)], two -coupled protons [ 6.48 (1H, , 2.2 Hz, H-8) and 6.26 (1H, , 2.2 Hz, H-6)], four aromatic protons of a 1,4-disubstituted benzene ring [ 7.84 (2H, , H-2' and H-6') and 7.01 (2H, , H-3' and H-5')] and two methoxy groups [ 3.89 and 3.88 (3H each, , 7-OCH and 4'-OCH)]. The C-NMR spectrum revealed 17 carbon signals corresponding to a conjugated carbonyl carbon [ 182.6 (C-4)], fourteen olefinic/aromatic carbons with five oxygenated carbons (δ 165.6, 164.2, 162.8, 162.4, 157.9), seven protonated carbons ( 128.2, 114.7, 104.5, 98.2, 92.8), two fully substituted carbons ( 123.8, 105.8) and two methoxy groups [ 55.9 and 55.7 (7-OCH and 4'-OCH)]. The spectral data suggested a flavone carrying a chelated hydroxy group at C-5 and two methoxy groups attached to C-7 and C-4'. A comparison of the NMR data of 2 with those of the reference17 suggested that 2 was 5-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone, which was previously reported in .
Compound 3 was obtained as yellow needles. The H-NMR spectrum had resonances for an aldehyde proton [δ 9.65 (1H, d, 7.8 Hz, H-9)], two trans-coupled protons [δ 7.40 (1H, d, 15.8 Hz, H-7), 6.60 (1H, dd, 15.8, 7.8 Hz, H-8)], three aromatic protons of a 1,2,4- trisubstituted benzene ring [δ 7.12 (1H, dd, 8.2, 1.9 Hz, H-6), 7.07 (1H, d, 1.9 Hz, H-2), 6.96 (1H, d, 8.2 Hz, H-5)], and a methoxy group (δ 3.95 (3H, s, 3-OCH)). The C-NMR spectrum showed resonances for 10 carbons, comprising an aldehyde carbonyl carbon [δ 193.9 (C-9)], two olefinic carbons [δ 153.4 (C-7), 126.9 (C-8)], a benzene ring and a methoxy group [δ 56.4 (3-OCH]. The benzene ring consists of three protonated carbons [δ 124.5 (C-6), 115.4 (C-5), 109.9 (C-2)] and three substituted carbons, two of which are oxygenated [δ 149.3 (C-3), 147.4 (C-4), 127.1 (C-1)]. The above spectral data revealed that the compound had a benzene ring with a conjugated aldehyde, a methoxy group and a hydroxy group. The compound was determined to be 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamaldehyde or coniferaldehyde (3) by comparison of the NMR spectral data with those published in the literature18.
Compound 4 was isolated as white crystals. The H- and C-NMR spectra closely resembled those of 3. There were resonances for a 1,3,4-trisubstituted benzene ring carrying two oxygenated carbons [δ 7.55 (2H, m, H-2' and H-6'), 6.96 (1H, d, 8.0 Hz, H-5'); δ 151.0 (C-4'), 146.9 (C-3'), 129.9 (C-1').123.8 (C-6'), 114.1 (C-5'), 109.8 (C-2')], and a methoxy group [δ 3.96 (3H, s, 3'-OCH); δ 56.3 (3'-OCH)]. The three carbons of the conjugated aldehyde in 3 were replaced by a carbonyl carbon of a ketone [δ 199.2 (C-1)], an oxymethylene group [δ 4.02 (1H, t, 5.3 Hz, H-3); δ 50.5 (C-3)] and a methylene group [δ 3.18 (1H, t, 5.3 Hz, H-2)]; δ 40.0 (C-2)]. The spectral data were consistent with those previously reported19, suggesting that compound 4 was 3-hydroxy-1-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one or -hydroxypropiovanillone, which was previously isolated from .
Compound 5 was obtained as white crystals. The H-NMR spectrum had resonances for the aldehyde proton [δ 9.85 (1H, s, H-7)] and four aromatic protons of a 1,4-trisubstituted benzene ring [δ 7.80 (2H, d, 8.5 Hz, H-2 and H-6), 7.00 (2H, d, 8.5 Hz, H-3 and H-5)]. The C-NMR spectrum showed resonances for a conjugated carbonyl carbon [δ 191.0 (C-7)], six aromatic carbons consisting of two pairs of protonated symmetrical carbons [δ 132.8 (C-2, C-6), 116.7 (C-3, C-5)], and two substituted carbons, one of which were oxygenated [δ 164.0 (C-4)]. The compound was therefore determined to be -hydroxybenzaldehyde (5)20.
Compound 6 was isolated as white needles. The H- and C-NMR spectra of 3 were very similar to those of compound 3. There were signals for an aldehyde [δ 9.74 (1H, s, H-7); δ 191.5 (C-7)], a 1,3,4-trisubstituted benzene ring carrying two oxygenated carbons [δ 7.43-7.41 (2H, m, H-2, H-6), 7.04 (1H, d, 6.6 Hz, H-5); δ 153.4 (C-3), 148.3 (C-4), 129.3 (C-6), 126.5 (C-1), 114.9 (C-5), 109.9 (C-2)], and a methoxy group [δ 3.91 (3H, s, 3-OCH); δ 55.0 (3-OCH)]. The only difference was that the signals for a carbon‒carbon double bond disappeared. A comparison of the NMR data with those in the literature21 suggested that compound 6 was vanillin (6).
Compounds 1--3 were evaluated for their in vitro cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells via the MTT assay, with ellipticine used as the positive control. The two polyphenol derivatives, palmarumycin JC2 (1) and coniferaldehyde (3), had very weak effects, with IC values of 36.09 and 53.20 µg/ml, respectively (ellipticine, IC = 0.45 µg/ml), whereas 5-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone(2) was inactive (IC > 256 µg/ml). Previously, palmarumycin JC2 (1) was reported to exhibit weak or no activity against the NCI-H187, BC, KB, and Vero cell lines22. The low cytotoxicity of the compound is consistent with our findings. This is the first report on the cytotoxicity of compounds 2 and 3.
Cytotoxicity of compounds 1-3 against HepG2 cells
|
Compound |
IC50 (µg/ml) |
IC50 (µM) |
|
Palmarumycin JC2 (1) |
36.09 ± 3.79 |
108.03 ± 11.35 |
|
5-Hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone (2) |
> 256 |
> 859 |
|
Coniferaldehyde (3) |
53.20 ± 4.37 |
298.88 ± 24.55 |
|
Ellipticine a |
0.45 ± 0.04 |
1.83 ± 0.16 |
CONCLUSION
Six phenolic compounds, palmarumycin JC2 (1), 5-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavone(2), coniferaldehyde (3), 3-hydoxy-1-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methoxyphenyl)propan-1-one (4), -hydroxybenzaldehyde (5) and vanillin (6), were isolated from the ethyl acetate of the bark of A. lawii. This is the first time that six compounds have been found in . The in vitro cytotoxicity of compounds 1--3 toward HepG2 cells was evaluated via the MTT assay. Nevertheless, the compounds exhibited very weak effects or no activity.
ABBREVIATIONS
NMR Nuclear magnetic resonance
CC Column Chromatography
COSY Correlation Spectroscopy
Doublet
Doublet of doublet
GPC Gel Permeation Chromatography
HMBC Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Coherence
HSQC Heteronuclear Single Quantum Correlation
HR-ESI-MS High Resolution Electron Spray Ionization Mass Spectroscopy
IC The Half maximal inhibitory concentration
IR Infrared
Coupling Constant
Multiplet
Quartet
RP Reversed-phase
s Singlet
Triplet
TLC Thin Layer Chromatography
COMPETING INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
Pham Hoang Quan, Ngo Trang Nhu Ngoc, Nguyen Dieu Lien Hoa: research ideas and project plans; Pham Hoang Quan, Nguyen Thi Thao Ly, Trinh Thi Dieu Binh, and Ngo Trang Nhu Ngoc: sample collection, extraction, isolation; structure elucidation; Pham Hoang Quan, Nguyen Dieu Lien Hoa: writing the article.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is funded by Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM), under Grant Number B2023-18-04.

