Synthesis of Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure towards the applications in visible light photodetectors
- University of Science, Viet Nam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- University of Science, Viet Nam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
Abstract
Introduction: 2D reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has become a key material in optoelectronic devices due to its outstanding electrical properties and stability. However, the application potential of rGO in such devices is still limited due to its low light absorption ability (especially in the visible region). Hence, this study aims to overcome this problem by synthesizing an Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure. Methods: Herein, while rGO was formed via a hydrazine vapor reduction, Ag and CuO were synthesized through simple, low-cost chemical techniques. Results: Our results revealed that compared to bare rGO and CuO/rGO samples, the hybrid Ag/CuO/rGO has remarkably higher absorption in the visible region. Besides, the fabricated Ag/CuO/rGO also demonstrated sensitivity toward blue light excitation, with good performance and stability. Conclusion: We hope that our study can further enable research on the application of rGO in the optoelectronic sector.
INTRODUCTION
Since its first discovery in 2004, graphene (Gr) and its derivatives, especially reduced graphene oxide (rGO), have become key materials in both industry and scientific research1. Owing to its outstanding electrical properties, this material is widely employed in high carrier mobility applications such as electronic devices and transparent electrodes2, 3, 4. Currently, rGO, a Gr derivative, is also a potential candidate in the optoelectronic field, especially photodetectors (PDs), because of its wide response to light excitation5. For example, the integration of rGO with conventional Si was proven to be a novel strategy for high-performance broadband photodiodes with fast response6. In addition, et al reported a photodetector based on rGO, which could operate in the visible region with a relatively fast response/recovery time and reasonable performance7. However, rGO still has some disadvantages that can hinder further innovation in optoelectronic applications. Specifically, rGO is prone to other environmental elements (e.g., gaseous substances, humidity, etc.), leading to a decrease in device selectivity8. Moreover, the performance of rGO-based devices is also detrimental because of the considerably low light absorption ability of rGO (especially in the visible region) and the high charge carrier recombination rate (due to high mobility)9, 10, 11. Therefore, modifying rGO to enhance the performance of PDs and other optoelectronic devices is still a research interest.
For years, various modification methods to increase the performance of rGO-based devices have been widely studied, and creating hybrid structures between rGO and other materials, i.e., metal oxides (MOs), has been considered an efficient way to obtain greater properties for the next generation of optoelectronic applications12, 13. Among the utilized MOs, such as zinc oxide (ZnO)14 and titanium dioxide (TiO)15, copper oxide (CuO) is among the most prevalent because of its abundance, high stability, and facile synthesis16, 17. For example, our group introduced a broadband photodetector based on the hybrid structure between rGO and CuO18. This rGO/CuO device structure not only revealed enhanced absorption compared with that of bare rGO but also exhibited acceptable performance over a wide range of wavelengths (from 395 nm to 945 nm). CuO was also demonstrated as one of the key components of a high-performance rGO-based MoS/rGO/CuO/ITO dual-band photodetector, with a responsivity and detectivity of up to 646.8 A W and 7.28×10 Jones, respectively19. Notably, scientists recently realized that noble metal nanostructures (i.e., Ag and Au nanostructures) with strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effects can significantly increase the absorption ability of rGO, especially in the visible region20, 21. and colleagues demonstrated that the hybrid structures between rGO and Ag/Au nanoparticles could provide an 8-to-20-fold enhanced detector performance compared with that of bare rGO22. From these views, combining rGO with metal oxides or noble metals is an effective route to overcome the disadvantages associated with the absorption ability or low performance of rGO.
On the basis of the aforementioned platforms, we aim to further improve the absorption ability of rGO-based hybrid structures by simultaneously combining rGO with two-dimensional (2D) CuO and Ag nanoparticles (Ag/CuO/rGO). In our structure, while rGO was reduced from GO via hydrazine vapor, 2D CuO and AgNPs were synthesized via simple chemical methods. These results indicate that we successfully synthesized a Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure with enhanced absorption ability, noticeably in the visible region, compared with that of bare rGO and CuO/rGO, which may be due to the strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect of the Ag nanoparticles. In addition, the fabricated Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector exhibited reasonable sensitivity to visible light illumination (464 nm), and cyclic testing under continuous turning on and off of light revealed the good stability of the device. We believe that this study can enable further study of rGO-based hybrid structures, which can be applied in advanced optoelectronic technologies in the future.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemical materials
The chemicals used in this experiment included copper(II) nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO).3HO, 99% purity, Sigma Aldrich), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 99% purity, Sigma Aldrich), silver nitrate (AgNO, 99% purity, Sigma Aldrich), graphene oxide nanoflakes (99% purity, Sigma Aldrich), acetone (CHO > 99,99% purity, Chemsol), ethanol (CHOH, 99,99% purity, Chemsol), and hydrazine hydrate solution (NHNH, 99,99% purity, Sigma Aldrich).
Experimental procedures
First, the rGO layer was synthesized via a reduction process. Indeed, GO (0.5 mg mL, dispersed in ethanol) was spray-coated on a precleaned glass substrate. Consequently, the GO-coated substrate was exposed to hydrazine (NHNH) vapor at 60°C for 18 hours to reduce the oxygen-containing functional groups of GO, resulting in the formation of an rGO layer, which was then subjected to heat treatment at 100°C.
2D CuO was synthesized through a hydrothermal technique. Initially, 0.24 g of Cu(NO).3HO was mixed with 0.4 g of NaOH in 100 mL of distilled water. After being stirred for 1 hour, the resulting solution underwent a hydrothermal process at 180°C for 4 hours. The hydrothermal product was subsequently filtered, washed several times with distilled water, and dried at 100°C for 6 hours to obtain 2D CuO nanosheets. Finally, 0.0025 g of CuO was dispersed in 5 mL of CHOH to prepare a 0.5 mg mL⁻¹ CuO solution for further experiments.
The Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure was synthesized as follows: after the reduction of GO to rGO on the glass substrate, the CuO dispersion was spin-coated at 300 rpm for 30 on the rGO layer, followed by a 1-h heat treatment at 100°C. Consequently, the CuO/rGO film was immersed in a solution containing 0.017 g of AgNO₃ dissolved in 9.5 mL of distilled water and 0.5 mL of C2H5OH under UV irradiation (λ = 295 nm, P = 35 W), which is suitable for the reduction of Ag to Ag. In the final step, the resulting sample was placed on a hot surface at 60°C until completely dry.
Device fabrication and characterization
After the synthesis of Ag/CuO/rGO on a glass substrate, silver electrodes were patterned via a sputtering technique via a shadow mask. This process resulted in a 1 mm Ag/CuO/rGO active channel with a length and width of 2 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively. The structural configurations of the synthesized samples were determined via X-ray diffraction (XRD) via a D8 Advance-Bruker diffractometer operating at 40 kV and 100 mA with Cu/Ka radiation (λ = 0.154 nm). Additionally, the optical properties of the photodetector were measured via an ultraviolet‒visible (UV‒Vis) spectrophotometer (JASCO V730). The surface morphologies of the hybrid materials were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4800). The photodetector characteristics, including I-V characteristics and I-t relationships, were investigated with a Keithley 2400 system and a 464 nm light source (model COBW1-480 from TOPAI).
RESULTS
A summary of our Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector fabrication process is depicted in Figure 1. Briefly, after the formation of the rGO charge transport layer on a precleaned glass substrate, 2D CuO was coated on the rGO surface via a spin-coating technique, followed by the decoration of Ag NPs via a UV reduction reaction. Finally, device fabrication was completed after the patterning of the silver electrodes.
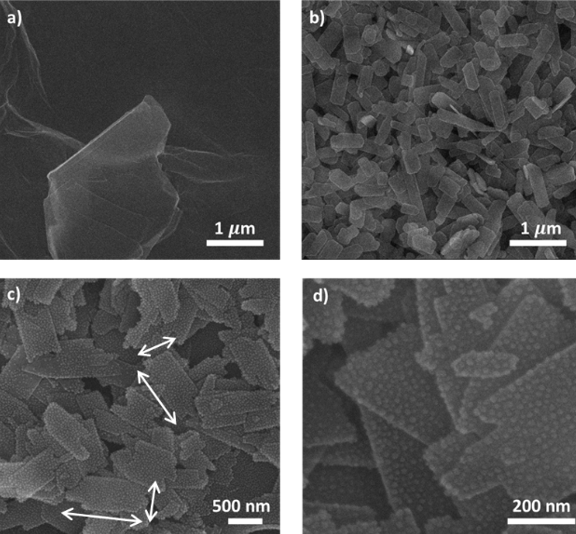
The morphologies of the rGO and Ag/CuO/rGO samples were observed through SEM images in Figure 2, where Figure 2a reveals the formation of rGO after reduction. Moreover, while the SEM image of CuO/rGO at a large scale (Figure 2b) shows the uniform distribution of 2D CuO plated on the rGO surface, the smaller-scale SEM images (Figure 2c-d) confirm the successful decoration of Ag NPs onto 2D CuO.

Device fabrication process

SEM images of (a) rGO at 1-μm scale (b) CuO/rGO at 1-μm scale and (c)-(d) Ag/CuO/rGO at 500-nm and 200-nm scale, respectively.

(a) XRD pattern of CuO/rGO (black line) and Ag/CuO/rGO (red line) samples and (b) UV‒Vis absorption spectra of rGO (black line), CuO/rGO (blue line), and Ag/CuO/rGO (red line) samples

Photoresponse behavior of Ag/CuO/rGO device. (a) I-V characteristic under dark and 464 nm illumination conditions and (b) Time-resolved photocurrent under 464 nm light excitation.

Cyclic time-resolved photocurrent of Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector under 464 nm

Energy band diagram of Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure under visible light illumination.
To confirm the formation of Ag NPs on the hybrid structure, X-ray diffraction patterns of the CuO/rGO and Ag/CuO/rGO samples are presented in Figure 3a. For both samples, a typical diffraction peak at 24.2°, corresponding to the (002) plane of rGO, was observed 23. Noticeably, this peak can be used to verify the successful formation of rGO after reduction since it is distinguished from the signature diffraction peak of GO, which is located at approximately 11°24. In addition, we also observed other peaks at 35.5°, 38.5°, 61.5°, 68.2°, and 75.1°, which represent the (002), (111), ( 13), and (220) planes of CuO25, 26, respectively, and a small peak at 38.2° of the (111) plane revealed the presence of Ag NPs in the Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure27.
The optical properties of the rGO, CuO/rGO, and Ag/CuO/rGO samples were evaluated via UV‒Vis absorption spectra, as shown in Figure 3b. For all 3 samples, the absorption peak at 263 nm is attributed to the intrinsic band edge absorption of rGO28. Compared with the typical absorption peak of GO at approximately 230 nm, this can also confirm our successful reduction from GO to rGO29. Notably, CuO/rGO has greater absorption in the visible region than does bare rGO, which may be due to the incorporation of CuO nanoplates. Interestingly, the Ag/CuO/rGO sample revealed a remarkable increase in visible absorption, which may be the result of the SPR effect of the Ag NPs.
To examine the potential of our Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure in photodetectors and optoelectronic applications, we fabricated a simple photoconductor and investigated its I‒V characteristics as well as its time-resolved photocurrent (as presented in Figure 4). Figure 4a shows that the Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector had good metal‒semiconductor Ohmic contact, and the measured current under light conditions was higher than that measured under dark conditions (please see the inset of Figure 4a). In addition, for the time-resolved photocurrent (Figure 4b), the changes in the photocurrent value when the light source is turned on and off also reveal the sensitivity of our hybrid device to light signals.
Cyclic testing under blue light (Figure 5) demonstrated that our Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector possesses relatively good repeatability and stability, indicating the potential of our proposed hybrid structure for realistic device fabrication.
DISCUSSION
Figure 2a shows that rGO formed thin sheets after being reduced from GO by hydrazine vapor. In addition, a large-scale SEM image of CuO/rGO (Figure 2b) demonstrated that 2D CuO plates with average widths and lengths of approximately 200–300 nm and 400–600 nm were uniformly distributed on the rGO surface after the spin coating process. Additionally, in the smaller-scale SEM images (Figure 2c-d), many small particles decorated on the 2D CuO nanoplates were found, which can be attributed to the presence of Ag NPs after the UV-reduction reaction.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the CuO/rGO and Ag/CuO/rGO samples (Figure 3a) were obtained to confirm the formation of Ag NPs on the hybrid structure. In both samples, along with the observed typical diffraction peaks of rGO and CuO (as presented in the results section), the appearance of the (111) peak of Ag NPs reveals the successful decoration of Ag NPs onto 2D CuO. Notably, the Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure was successfully fabricated, and our modification did not cause any serious damage to the structural properties of the materials, as no exotic peak was detected in the XRD analysis.
According to the UV‒Vis results (Figure 3b), the higher absorption in the visible region of CuO/rGO and Ag/CuO/rGO in comparison with that of the bare rGO sample can be attributed to the incorporation of CuO nanoplates. This result is similar to that of our previous study on a CuO/rGO hybrid photodetector . Furthermore, the noticeable increase in the visible absorption (wavelength range of approximately 400 nm to more than 600 nm) of the Ag/CuO/rGO sample demonstrates the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) phenomenon, which is a typical effect of noble metal nanostructures30, revealing the potential of our three-component hybrid structure for visible light detection.
In terms of the I‒V characteristics (Figure 4a), the symmetric linear current‒voltage relationship under both forward and reverse applied bias of the Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector reveals good metal‒semiconductor Ohmic contact31, and the increase in current under light conditions compared with dark conditions confirms the device response to light excitation. Moreover, from Figure 4b, the increase and decrease in the photocurrent when the blue light was turned on and off during excitation can be attributed primarily to the SPR effect, which will be further discussed later. Herein, the response and recovery times, which are defined as the time for the photocurrent to reach 90% of its maximum and the time to return to approximately 10% of the highest value32, were estimated to be 28 s and 59 s, respectively. Furthermore, we also calculated the responsivity (R), the critical performance parameter of a photodetector, which represents the ratio between the photocurrent and the excitation power density33. By using the formula , where and are the currents measured under light and dark conditions,respectively, P is the light power density (53 mW cm), A represents the area of the active channel (1 mm), and R was calculated to be 2.8 mA W. We believe that the values of the response/recovery time and responsivity are acceptable compared with those reported in previous studies on photodetectors based on similar materials.
Figure 5 shows the good repeatability and stability of our Ag/CuO/rGO device, where the photocurrent current increased when light was provided and decreased when the light was turned off without any significant changes in the recorded signals after several testing cycles. Notably, the baseline current through the device slightly increased after some cycles, which may be due to the existence of defects on the material surface. Indeed, these defects can trap charge carriers, hindering their recombination34. However, we believe that these results still indicate that Ag/CuO/rGO has potential for further research in the optoelectronic field and for practical device applications.
We clarified the photosensing mechanism of the Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector. Specifically, in this hybrid structure, rGO serves as a charge transport layer, 2D CuO with a large surface area effectively supports the decoration of Ag NPs and photon collection, and Ag NPs play a role in charge carrier generation due to their strong SPR effect. Indeed, under visible light illumination (Figure 6), the electron clouds on the surface of Ag NPs oscillate at a specific frequency. When the light frequency matches the frequency of the electron clouds, these clouds undergo resonance oscillation, and the electrons become highly energetic (known as “hot electrons” in the SPR state)35, 36, 37. Since the SPR state is higher than the conduction band (CB) of 2D CuO, the “hot electrons” can easily transfer from Ag NPs to 2D CuO and then further transport to rGO, increasing the Fermi level of this material. Finally, these electrons are driven to silver electrodes, generating a photocurrent through the hybrid device.
CONCLUSION
In summary, we have successfully synthesized a Ag/CuO/rGO hybrid structure via simple, low-cost chemical processes. Compared with those of the bare rGO and CuO/rGO samples, the Ag/CuO/rGO sample demonstrated a significantly greater absorption ability in the visible region. In addition, the as-fabricated Ag/CuO/rGO photodetector also exhibited sensitivity to visible light illumination (blue light, 464 nm), and cyclic testing revealed its good stability when the light source was turned on or off. Additionally, the photoresponse mechanism toward blue light, which was primarily the result of the SPR effect, was clarified. We believe that our study can enable further research on rGO-based hybrid structures for optoelectronic applications in the future.
Abbreviations
CB: conduction band, GO: graphene oxide, MOs: metal oxides, PDs: photodetectors, R: responsivity, rGO: reduced graphene oxide, SEM: scanning electron microscope, SPR: surface plasmon resonance, VB: valence band, XRD: X-ray diffraction
Acknowledgments
This research is funded by Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under grant number B2023-18-14.
Author contributions
D. A. Ngo: carried out the experiment on rGO, 2D CuO, and Ag NPs, writing the manuscript. N. M. Nguyen: writing the manuscript, analyzed I-V and I-t. T. P. Tran, G. V. Le: measured I-V, I-t, measured and analyzed XRD results. L. T. Duy: reviewed and edited the manuscript. C. K. Tran: measured, analyzed UV-Vis data. P. P. H. La: measured and analyzed SEM images. V. Q. Dang: conceptualization, supervised the experiment, and edited the manuscript.
Funding
The Funding was supported by Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM)
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

