Physical-chemical and electrochemical properties of sodium ion conducting polymer electrolyte using copolymer poly(vinylidene fluoride- hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP)/ polyethylene oxide (PEO)
- Key laboratory of Applied Physical Chemistry (APCLAB), VNUHCM-University of Science
- Department of Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, VNUHCMUniversity of Science
- 1. Key laboratory of Applied Physical Chemistry (APCLAB), VNUHCM-University of Science 2. Department of Physical Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, VNUHCMUniversity of Science
Abstract
Introduction: Polymers acting as both an electrolyte and a separator are of tremendous interest because of their many virtues, such as no leakage, flexible geometry, excellent safe performance, and good compatibility with electrodes, compared with their liquid counterparts. In this study, polymer electrolyte membranes comprising of poly(vinylidene fluorine-co-hexafluoropropylene) [PVDF-HFP] were plasticized with different mass ratios of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) in 1 M NaClO4/PC solutions, and were prepared and characterized in sodium-ion battery.
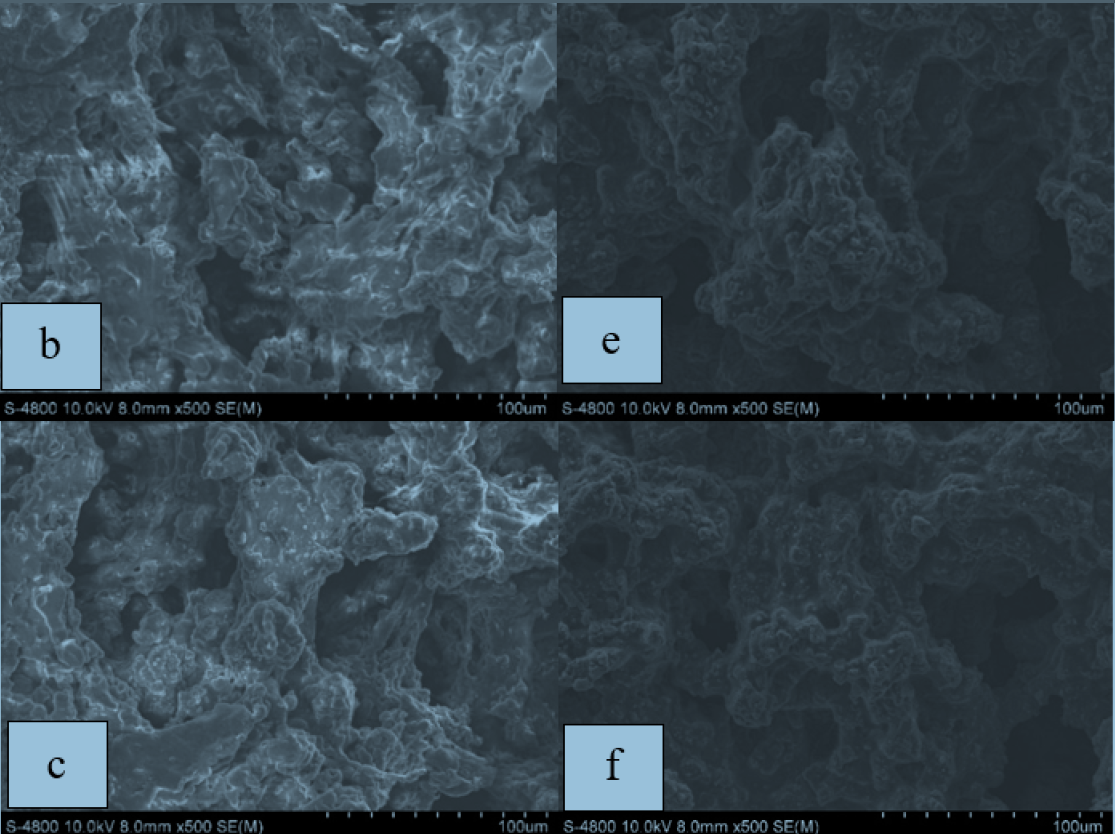
Methods: Polymer electrolyte membranes were prepared by solution-casting techniques. The membranes' performance was evaluated in terms of morphology, conductivity, electrochemical stability, thermal properties and miscibility structure. The following various characterization methods were used: Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), impedance spectroscopy (for determination of electrolyte resistance), cyclic voltammetry, thermal degradation analysis, and infra-red spectroscopy (for determination of structure of co-polymer).
Results: It was indicated that the PVDF-HFP/PEO membrane with 40 % wt. PVDF-HFP absorbed electrolytes up to 300 % of its weight and had a roomtemperature conductivity of 2.75 x 10-3 Scm-1, which was better than that of pure PVDF-HFP. All polymer electrolyte films were electrochemically stable in the potential voltage range of 2-4.2 V, which could be compatible with 3-4 V sodium material electrodes in rechargeable sodium cells.
Conclusion: The PVDF-HFP/PEO polymer electrolyte film is a potential candidate for sodium-ion battery in the potential range of 2-4.2 V.

