A deep learning model of major consulting support
- International University, Vietnam National University of HoChiMinh City, Vietnam
- International University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Abstract
Introduction: Major selection is always a matter of concern for students who have just graduated from high school and parents who have children to go to universities. Currently, there are many students who selected the wrong major, leading to unexpected learning results and wasting time and money. In fact, many students do not know which majors they are suitable for. The paper proposes a model of decision-making support in choosing majors for students immediately after graduating from high school using deep learning.
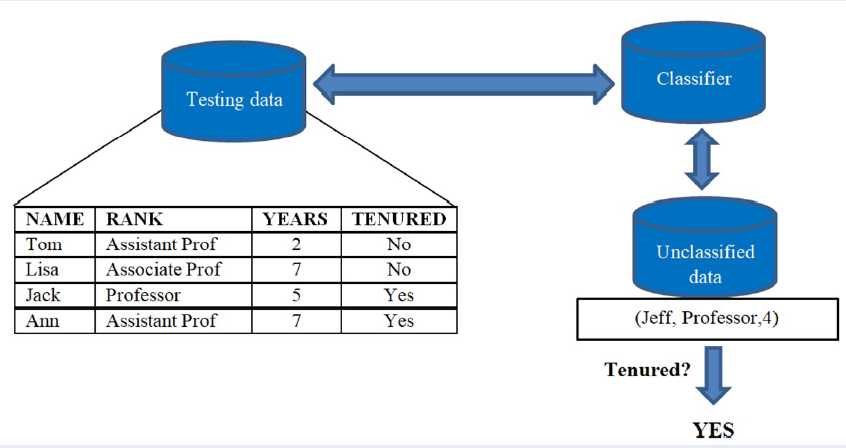
Methods: The model applied the XGBoost algorithm to build a decision tree for classification, mining educational data from which the student's ability and learning propensity are predicted and the appropriate majors are suggested.
Results: The data used for the system are collected from 1709 students’ results at the high school, the survey results on personal interests and personality, the teacher's comments and the results on major selection after graduation. From these data, the authors have built a model to advise students choosing the right major to continue their higher education.
Conclusion: The model is evaluated and verified through actual experiments with a high accuracy of 86% and proves the contribution of deep learning models to education.

